杨氏模量(Young's modulus)
摘要
杨氏模量是衡量物质材料在弹性范围内抗拉或抗压的物理量,其大小反映了材料的刚性。杨氏模量的测定对于研究各种材料的力学性质具有重要意义,并广泛应用于机械、生物力学、地质等领域。常见的测量杨氏模量的方法包括拉伸法、梁弯曲法、振动法等,同时也出现了新的技术和方法,如利用光纤位移传感器、莫尔条纹等进行测量。
正文
杨氏模量(Young's modulus)是表征在弹性限度内物质材料抗拉或抗压的物理量它是沿纵向的弹性模量。1807 年因英国医生兼物理学家托马斯 杨(Thomas Young, 1773-1829) 所得到的结果而命名。根据胡克定律在物体的弹性限度内应力与应变成正比比值被称为材料的杨氏模量它是表征材料性质的一个物理量仅取决于材料本身的物理性质。杨氏模量的大小标志了材料的刚性。
杨氏模量的测定对研究金属材料、光纤材料、半导体、纳米材料、聚合物、陶瓷、橡胶等各种材料的力学性质有着重要意义还可用于机械零部件设计、生物力学、地质等领域。

测量杨氏模量的方法一般有拉伸法、梁弯曲法、振动法、内耗法等还出现了利用光纤位移传感器、莫尔条纹、电涡流传感器和波动传递技术微波或超声波等实验技术和方法测量杨氏模量。


Young's modulus can vary somewhat due to differences in sample composition and test method.The rate of deformation has the greatest impact on the data collected, especially in polymers. The values here are approximate and only meant for relative comparison.


Sponsored Links
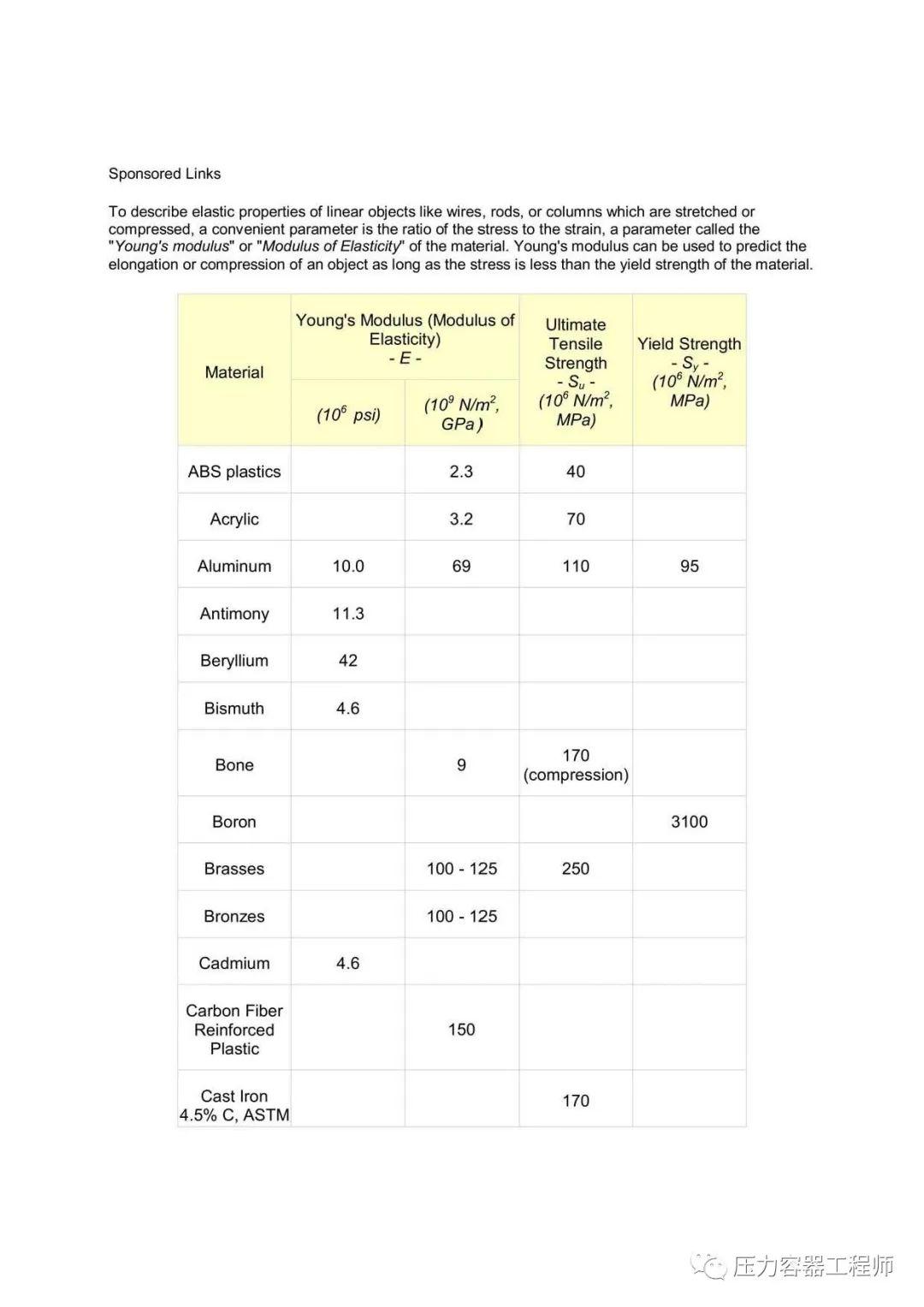
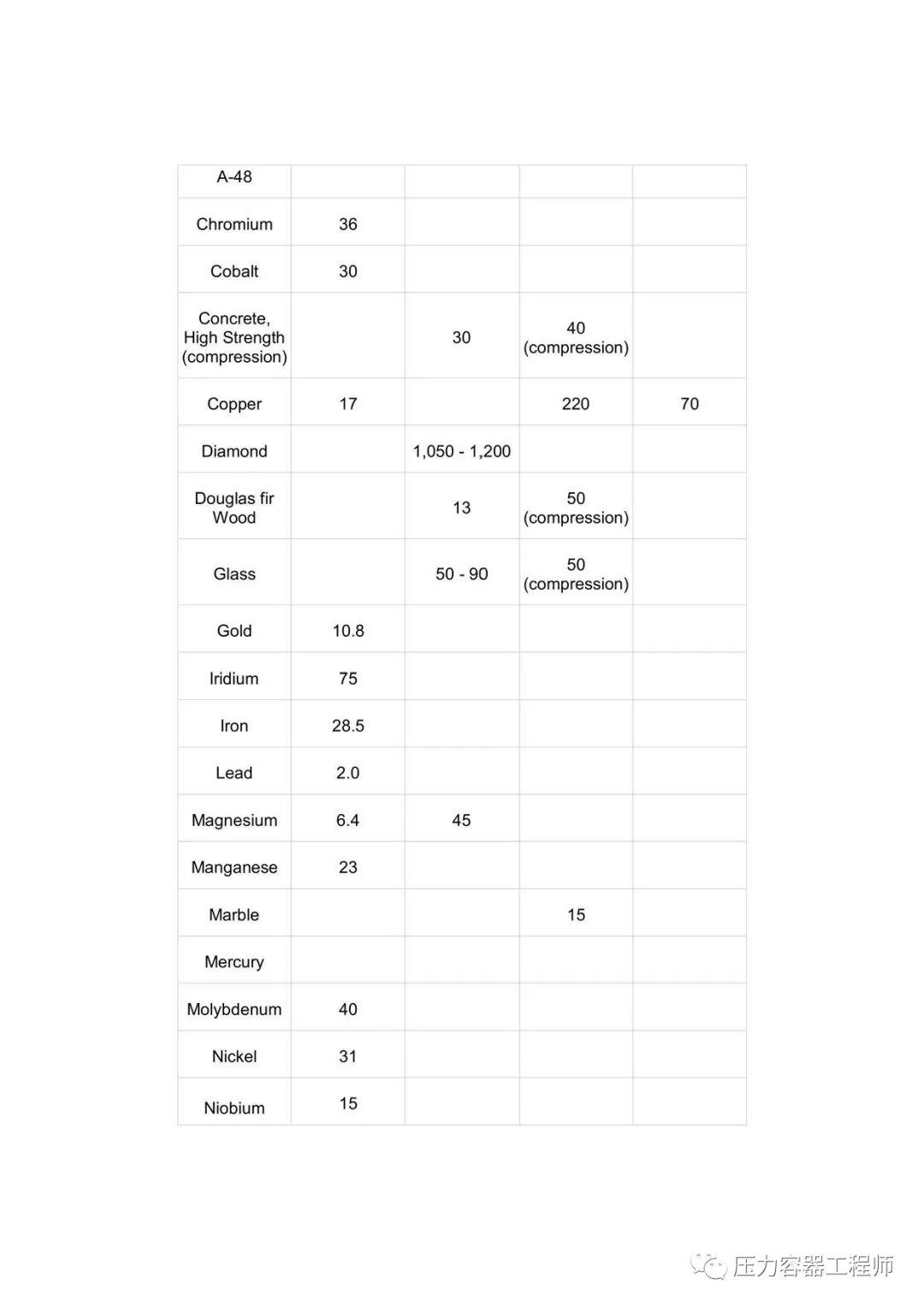
To describe elastic properties of linear objects like wires, rods, or columns which are stretched or compressed, a convenient parameter is the ratio of the stress to the strain, a parameter called the "Young's modulus" or "Modulus of Elasticity" of the material. Young's modulus can be used to predict the elongation or compression of an object as long as the stress is less than the yield strength of the material.