海洋平台防爆墙结构分析之SDOF方法和有限元分析方法


一、写在前面

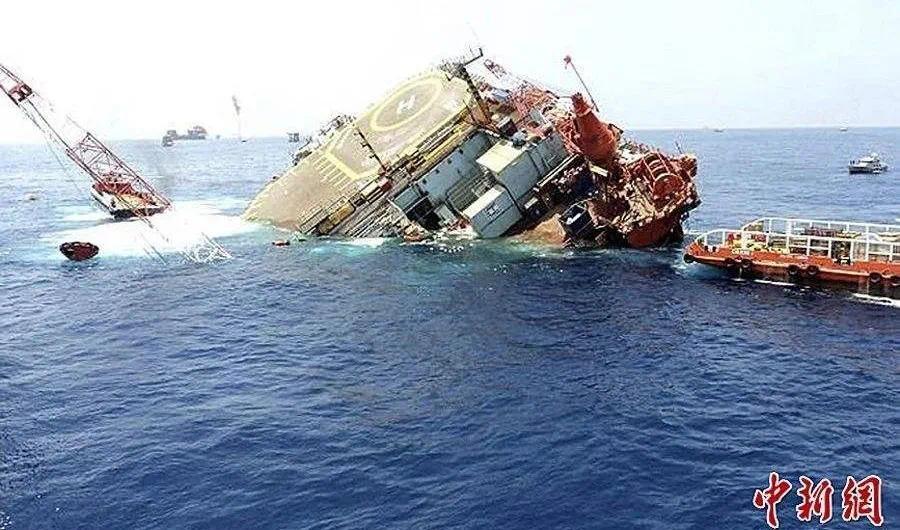
Deepwater Horizontal explosion(2010)
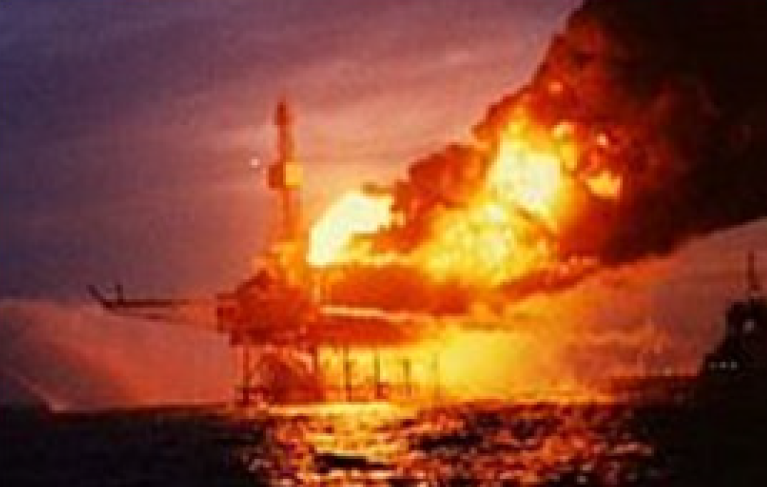

Piper Alpha explosion(1988)
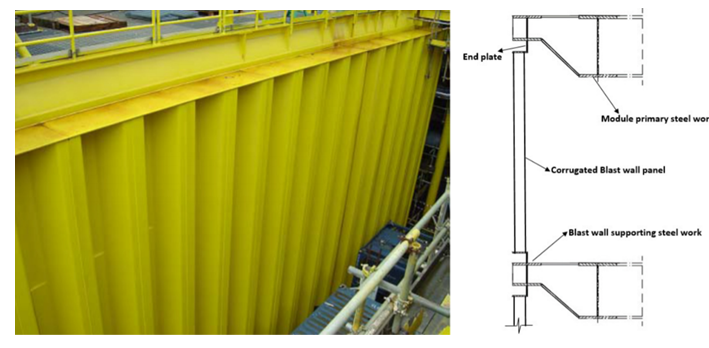
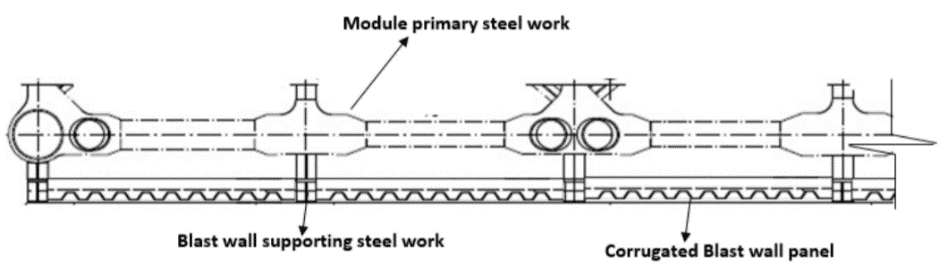
防爆墙结构不应作为承重墙,由大结构支撑
防爆墙结构设计主要考虑是“吸收”爆炸能量,而不是硬碰硬的“抵抗”。能量主要转换为塑性变形能和振动耗散。
防爆墙结构应该简单、轻质且易于维护。控制防爆墙的重量对平台整体重量控制十分重要。
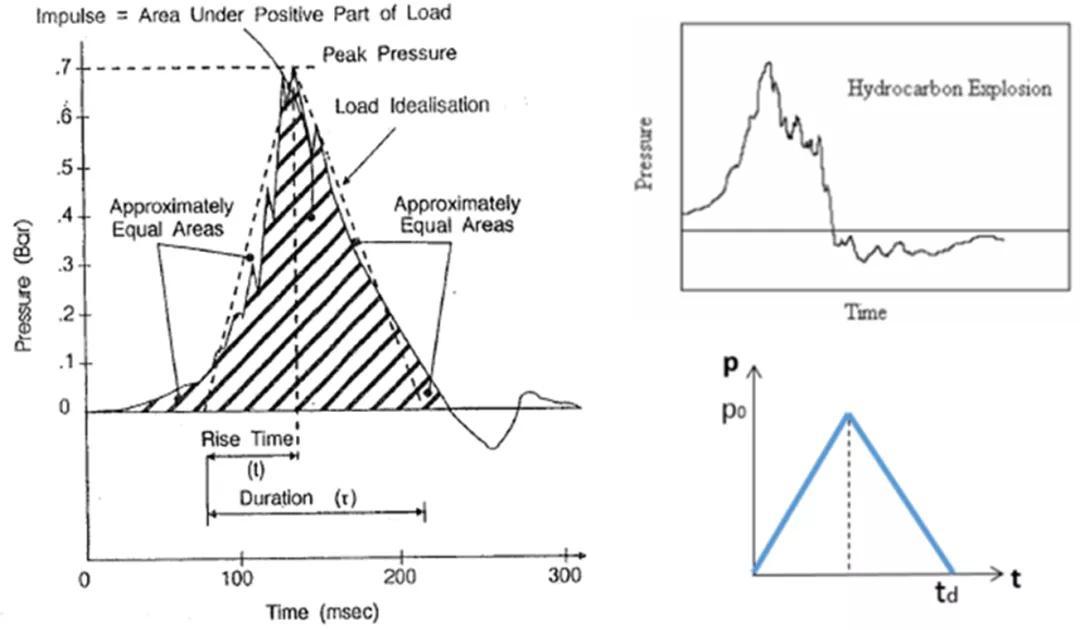
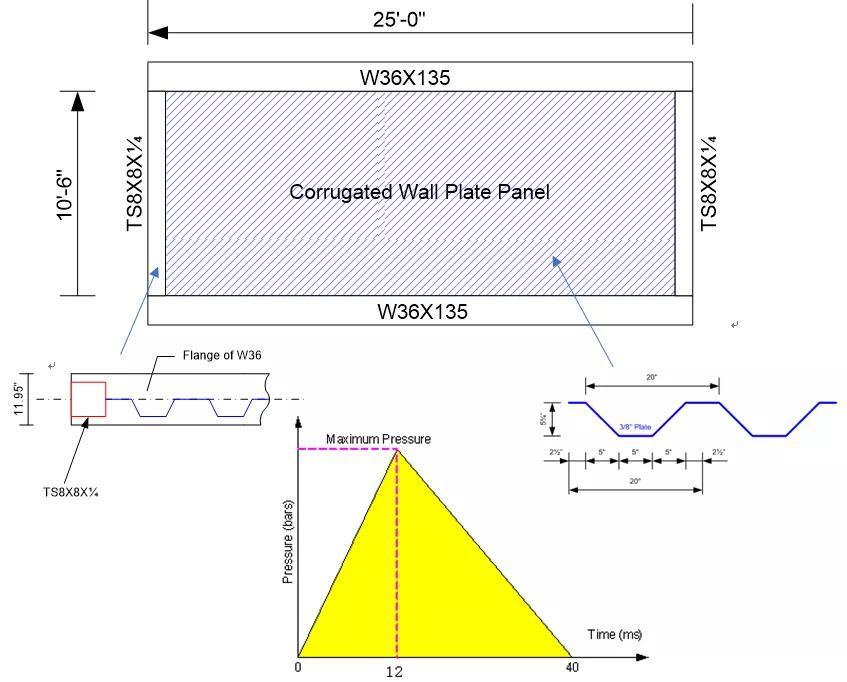
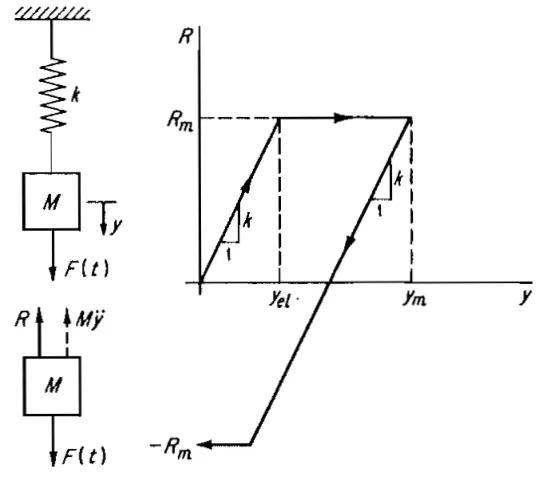
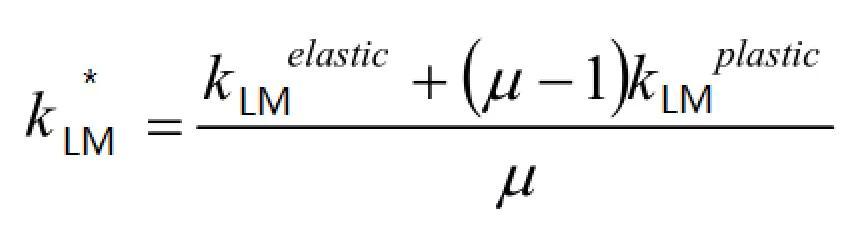


在基本解的基础上,可以考察更复杂的因素,如材料的动力硬化、爆炸载荷的“负压”阶段、剪切的影响、“膜”应力的影响、边界条件的影响等等。
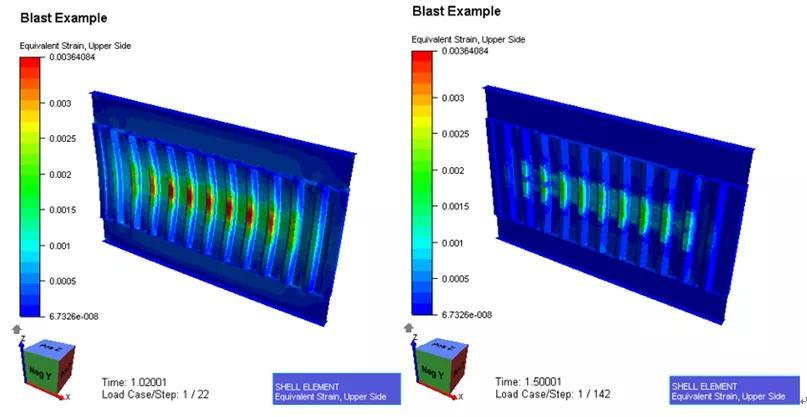
可以更真实的反映结构整体的刚度和相互作用,尤其是槽型壁各槽条之间多样的模态形式。这是简单梁和等效SDOF系统难以考虑的。
可以更直观的检查塑性应变和范围。塑性应变是衡量结构是否仍然有效的重要衡准。一般焊接处控制在5%以内,非焊接处在10%左右。
可以结合更高级的CFD流固耦合计算得到更为接近实际的载荷时历,进一步优化设计。

学习型仿真工程师 船舶与海洋工程院校学生 从事海工平台设计工作的工程师 从事海工平台结构强度规范校核和有限元强度评估的工程师 船厂现场详细设计工程师
系统学习《海洋平台强度分析》这门经典课程
深入理解各类海洋平台结构的分析要点和思路,重视通过手算和梁系计算预先对有限元仿真的结果���初步判断和定性分析,提高分析效率和准确性。
从“老法理”的角度分析结构问题,讲解工程案例、各大主流规范背景和出发点,知其然更知其所以然。
本课程学习包含练习实践课程,介绍了用梁系软件Dlubal RSTAB和当下流行的Python编程软件来分析解决问题。
学习本课程可以为工程仿真工作打下坚实基础,减少盲目仿真,加强对仿真结果的分析和判别能力。课程的理念是让仿真计算不仅仅是完成任务的工具,更是提升自己能力的手段。
订阅用户讲师一对一答疑专栏服务,还可以获得课程有关的资料进行练习,其他用户,关注本公众号,在对话框回复 小助手 申请进入海工群进行交流。也可以添加微信【fangzhenxiu999】咨询。
3、讲师介绍
4、附赠Python迭代小程序
# Python Codeimport numpy as np # Python强大的numpy模块搞定基本函数from scipy import interpolate # Python强大的scipy模块搞定插值# 定义设计曲线 (Rm/F1=1.0)# List x=td/T# List y=Ym/Yelx=[0.11312,0.17313,0.2571,0.4074,0.58394,0.79807,1.0504,1.3964,1.773,2.3566,2.685,3.0976,3.3961,3.7356,4.2567,4.8228,5.6064,6.2329,6.5401,6.8434,7.2125,7.8135,8.7628,9.8677,]y=[0.29923,0.45155,0.6526,0.9747,1.2727,1.5763,1.834,2.1859,2.1054,1.5665,1.2086,0.946,0.9265,1.0447,1.2724,1.3661,1.0901,0.9006,0.8756,0.9799,1.122,1.2672,1.3025,1.1459,]# 定义二次样条插值函数f=interpolate.interp1d(x,y,kind='quadratic')# 定义基本参数td=0.04KLM_e=0.78KLM_p=0.66Mt=154k=10233662# 定义初始迭代的uu=1.8# 定义迭代函数def iteration(u_old): # define iteration functionKLM = (KLM_e + (u_old-1)*KLM_p)/u_oldT = 2*np.pi*(KLM*Mt/k)**0.5tau = td/Tu_new = f(tau)return u_new# 调用循环体来迭代while True:UU = iteration(u)if np.abs((UU-u)/u)<=0.001: # Set 0.1% as criteriabreak # stop iteration if criteria is fulfilledelse:u = UU # update u and continue the iterationcontinueprint (u) # 打印结果,u=1.99
作者:Simon 仿真秀专栏作者
登录后免费查看全文
著作权归作者所有,欢迎分享,未经许可,不得转载
首次发布时间:2020-08-20
最近编辑:5年前
作者推荐
免费
5.0
相关推荐
最新文章






