VTK库学习 | 百万级自由度有限元模型云图绘制只需0.02秒!
温馨提示:本文字数9235,16副插图,预计阅读时间24分钟。
Python广受大家喜爱的重要原因是它有很多优秀的库,直接调用即可。针对有限元分析过程中云图的绘制,木木找了了一个非常好用的库—PyVista。PyVista是一个用于可视化工具包(VTK)的辅助模块,通过NumPy和各种方法和类提供了对VTK库的包装和直接数组访问。
项目地址:https://docs.pyvista.org/version/stable/user-guide/,该项目很容易上手,接下来教大家如何把玩这个好玩的工具!


今天的分享需要读者了解vtk的一些基础语法知识,想看历史文章:自编有限元程序如何与Paraview进行梦幻联动?,本次分享的案例数据文件都可以在知识星球内提供的《有限元基础编程百科全书》链接内下载。

官网第一个小案例
首先,先pip安装pyvista:
pip install pyvista
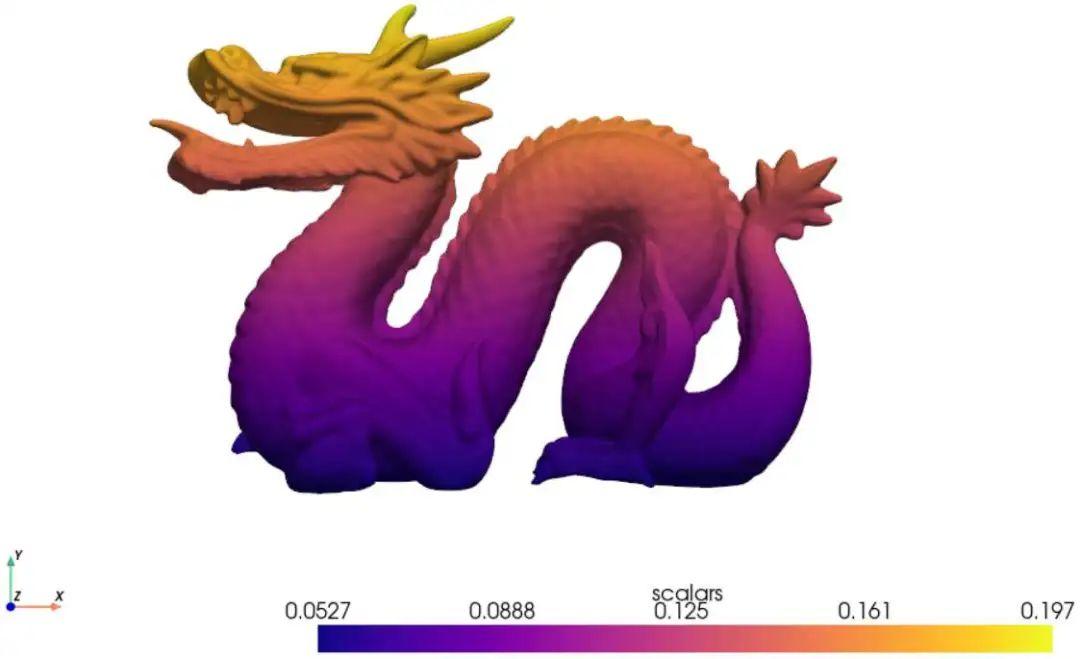
龙年先为大家画个龙年吧,官网提供的源程序只有4行,导入案例中的mesh信息,获取vtk语法中的scalars,指定绘图显示视图方向和cmap,直接出图,就是这么炫酷!
from pyvista import examples
mesh = examples.download_dragon()
mesh['scalars'] = mesh.points[:, 1]
mesh.plot(cpos='xy',cmap='plasma')
官网有非常详细的帮助文档,都是英文显示,如果大家不想去看,木木在这里整理了一些有限元云图方面常用的一些绘图设置,主要包括以下几个方面:
网格数据结构 绘图方法 云图显示 自定义绘图模板 自定义colorbar 载荷箭头、约束信息绘制 方向标志 大自由度模型测试
网格数据结构
pyvista可支持PolyData数据结构和vtk数据结构,本节先展示PolyData数据如何绘制,我主观不建议这样搞,强烈建议导入vtk文件!有关PolyData的解释可详见——https://docs.pyvista.org/version/stable/user-guide/data_model。
import pyvista as pv
import numpy as np
points = np.array([[0, 0, 0], [1, 0, 0], [0.5, 0.5, 0]])
cells = [[3, 0, 1, 2]]
mesh = pv.PolyData(points, cells)
mesh.plot(cpos='xy',show_edges=True)

以上绘制方法,我觉得颇为繁琐,不如将有限元结果写为.vtk文件,然后导入即可,之前我们是借助Paraview实现云图,现在我们直接调用pyvista进行绘制,可以达到Paraview同样的效果,且支持高度定制。使用pyvista.read(vtkfilename)进行读取,
mesh = pv.read('C3D8.vtk')
print('node number = ',mesh.n_points)
print('element number = ',mesh.n_cells)
print('node coordinate = ',mesh.points[0])
print('point_data = ',mesh.point_data)

查看有单元数: mesh.n_cells查看节点数: mesh.n_points节点坐标: mesh.points单元编码: mesh.cells(缩并为一维数组)查看SCALARS(云图变量种类)数: mesh.n_arrays查看point data有哪些: mesh.point_data查看point data 具体的值: mesh.point_data[’Displacement’]查看cell data有哪些: mesh.cell_data查看cell data 具体的值: mesh.cell_data[’AxialForce’]也可以直接查看: mesh[’Displacement’]或mesh[’AxialForce’]也可以自行添加cell data或者point data : mesh.cell_data[’test’] = np.random.rand(mesh.n_cells)
绘图方法
绘图方法有两种:mesh.plot和pyvista.Plotter.add_mesh,个人喜欢后者,因为可以不断增添新特征,让我们看一下两者的效果吧,以后的教学都以后者为基础。
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
mesh = examples.load_airplane()
mesh.plot()

import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import examples
mesh = examples.load_airplane()
plotter = pv.Plotter()
plotter.add_mesh(mesh)
plotter.show()
云图显示
以绘制节点位移云图为例,分享pyvista的各种花式绘图技巧,在以下代码中展现了:C3D8单元的云图绘制、节点显示、单元边界显示、节点编号显示。
import pyvista as pv
mesh = pv.read('C3D8.vtk')
dargs = dict(
scalars="Displacement",
show_scalar_bar=False,
show_vertices=True,
show_edges=True,
vertex_color='red',
point_size=15,
)
pl = pv.Plotter(shape=(2, 2))
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),**dargs)
pl.add_text("Magnitude Displacement", color='k')
pl.subplot(1, 0)
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),component=0, line_width=2,**dargs)
pl.add_text("X Displacement", color='k')
label_coords = mesh.points
pl.add_point_labels(label_coords, [f'{i+1}' for i in range(mesh.n_points)],
font_size=25, point_size=5)
pl.subplot(0, 1)
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),component=1,render_points_as_spheres=True,**dargs)
pl.add_text("Y Displacement", color='k')
pl.subplot(1, 1)
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),component=2,**dargs)
pl.add_text("Z Displacement", color='k')
pl.show()

以上Python语句,相信大家只要稍微看一下就能明白,在绘图的时候可以单独设置绘图参数,比如这样:plotter.add_mesh(mesh,scalars=’Displacement’,component=0,也可以使用上述代码的形式,将绘图参数集中在drags的设置中。注意有以下几点:
component=0表示第一个分量,如果不设置的话,就表示合量Magnitude;上图的节点显示看上去有很多没有显示,在实际绘图过程中,将图片逐渐放大后,每个节点的编号都会显示出来; render_points_as_spheres=True表示将点的形状转换为3D圆球状,更具观赏性;show_scalar_bar=False是为了后续定制colorbar,如果不设置为False,后面在你定制colorbar时,将会出现两个colorbar。
自定义colorbar
本小节将会分享如何自定义云图中的colorbar以及cmap,让云图的样式更漂亮一点。
import pyvista as pv
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
colors = [
[0, 0, 255], [0, 93, 255], [0, 185, 255], [0, 255, 232],
[0, 255, 139], [0, 255, 46], [46, 255, 0], [139, 255, 0],
[232, 255, 0], [255, 185, 0], [255, 93, 0], [255, 0, 0]
]
colors = np.array(colors)/255.0
custom_cmap = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('custom_cmap', colors, N=12)
mesh = pv.read('C3D8.vtk')
dargs = dict(
scalars="Displacement",
show_scalar_bar=False,
show_vertices=True,
show_edges=True,
edge_color='#000080',
vertex_color='red',
point_size=15,
cmap = custom_cmap,
render_points_as_spheres=True
)
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),**dargs)
pl.add_scalar_bar(title="U",n_labels=13,n_colors=12,fmt='%.3e',vertical=True,
width=0.05,position_x=0.03, position_y=0.5,font_family='times')
pl.show()

值得注意的是:
n_labels=13和n_colors=12表示colorbar上面分几段显示字,分几段显示颜色custom_cmap是自定义的色谱,在这里我设置了12种颜色,色谱和Abaqus默认色谱保持一致,读者也可以设置其他python内置的cmap,如:jetwidth=0.05表示colorbar的宽度,数值代表画幅的相对比例position_y=0.5表示colorbar底面距离画幅底面的比例
自定义绘图模板
在设置绘图参数时,可以通过设置drags,也可以自定义绘图模板,下面给出的代码注释已写的非常清楚。
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import pyvista as pv
import numpy as np
from pyvista import themes
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
# 自定义色谱
colors = [
[0, 0, 255], [0, 93, 255], [0, 185, 255], [0, 255, 232],
[0, 255, 139], [0, 255, 46], [46, 255, 0], [139, 255, 0],
[232, 255, 0], [255, 185, 0], [255, 93, 0], [255, 0, 0]
]
colors = np.array(colors)/255.0
# N表示色谱离散程度
custom_cmap = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('custom_cmap', colors, N=12)
my_theme = pv.plotting.themes.DocumentTheme() # 开始自定义绘图模板
my_theme.cmap = custom_cmap # 使用自定义的custom_cmap
my_theme.show_edges = True # 单元边界显示
my_theme.show_vertices=True # 节点显示
my_theme.render_points_as_spheres=True # 节点显示转换为3D圆球
my_theme.edge_color='#000080' # 单元边界的颜色
my_theme.line_width=1 # 单元边界宽度
my_theme.background = 'white' # 背景颜色
my_theme.colorbar_vertical.width = 0.05 # colorbar宽度
my_theme.colorbar_vertical.position_x=0.03 # colorbar 位置
my_theme.colorbar_vertical.position_y=0.5 # colorbar 位置
my_theme.opacity=1 # 透明度 0~1
my_theme.nan_color = 'darkgray' # 无穷大值的颜色显示
my_theme.window_size = [700, 500] # 画幅尺寸
my_theme.font.family = 'times' # 字体族
my_theme.title = 'FEA Result' # 画幅名字
pv.global_theme.load_theme(my_theme) # 加载自定义模板
mesh = pv.read('C3D8.vtk')
dargs = dict(
scalars="Displacement",
show_scalar_bar=False,
vertex_color='red',
point_size=15,
)
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),**dargs)
pl.add_scalar_bar(title="U",n_labels=13,n_colors=12,fmt='%.3e',vertical = True)
pl.show()
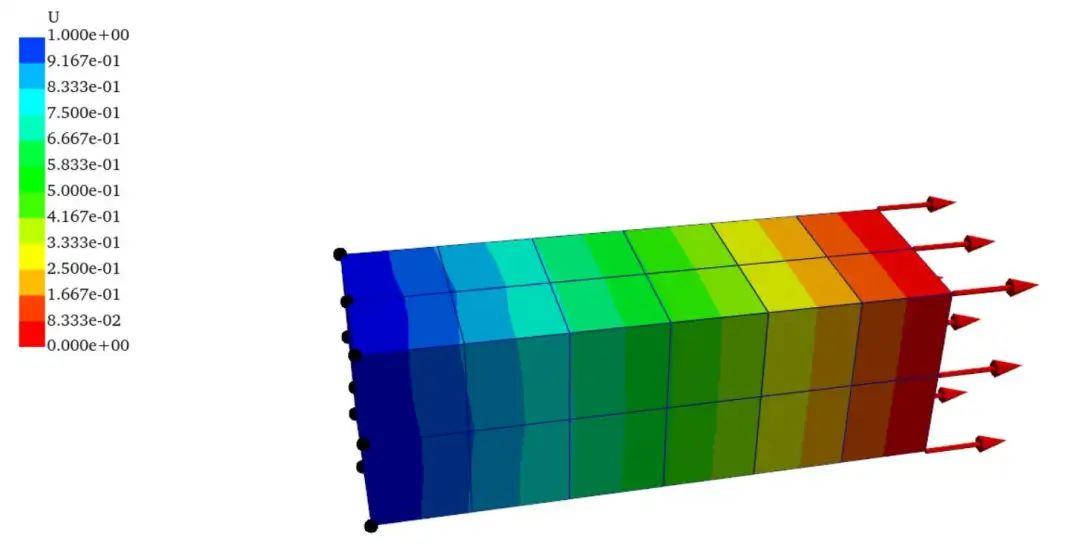
载荷箭头、约束信息绘制
为了显示边界条件的施加,我们可以添加箭头显示,值得注意的是,如果在主题模板中将show_edges设置为True,则全部的模型都讲显示边界,在这里为了美观,将箭头的边界线隐藏,在主题模板中将show_edges设置为False,模型的边界线在drags中设置。
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
import pyvista as pv
import numpy as np
from pyvista import themes
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
# 自定义色谱
colors = [
[0, 0, 255], [0, 93, 255], [0, 185, 255], [0, 255, 232],
[0, 255, 139], [0, 255, 46], [46, 255, 0], [139, 255, 0],
[232, 255, 0], [255, 185, 0], [255, 93, 0], [255, 0, 0]
]
colors = np.array(colors)/255.0
# N表示色谱离散程度
custom_cmap = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('custom_cmap', colors, N=12)
my_theme = pv.plotting.themes.DocumentTheme() # 开始自定义绘图模板
my_theme.cmap = custom_cmap # 使用自定义的custom_cmap
my_theme.show_edges = False # 单元边界显示
my_theme.show_vertices=False # 节点显示
my_theme.render_points_as_spheres=True # 节点显示转换为3D圆球
my_theme.edge_color='#000080' # 单元边界的颜色
my_theme.line_width=1 # 单元边界宽度
my_theme.background = 'white' # 背景颜色
my_theme.colorbar_vertical.width = 0.05 # colorbar宽度
my_theme.colorbar_vertical.position_x=0.03 # colorbar 位置
my_theme.colorbar_vertical.position_y=0.5 # colorbar 位置
my_theme.opacity=1 # 透明度 0~1
my_theme.nan_color = 'darkgray' # 无穷大值的颜色显示
my_theme.window_size = [700, 500] # 画幅尺寸
my_theme.font.family = 'times' # 字体族
my_theme.title = 'FEA Result' # 画幅名字
pv.global_theme.load_theme(my_theme) # 加载自定义模板
mesh = pv.read('C3D8.vtk')
dargs = dict(
scalars="Displacement",
show_scalar_bar=False,
show_edges = True,
vertex_color='red',
point_size=15,
)
pl = pv.Plotter()
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(),**dargs)
Force_node = mesh.points[range(0,9)]
Fix_node = mesh.points[range(54,63)]
direction = np.tile(np.array([1, 0, 0]), (len(Force_node), 1))
pl.add_arrows(Force_node, direction, mag=10, color='red')
pl.add_points(Fix_node, color='black',point_size=15)
pl.add_scalar_bar(title="U",n_labels=13,n_colors=12,fmt='%.3e',vertical = True)
pl.show()
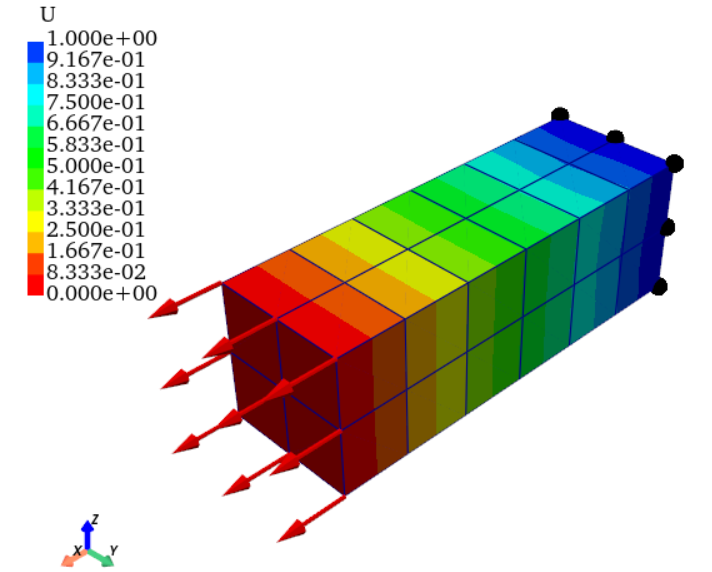
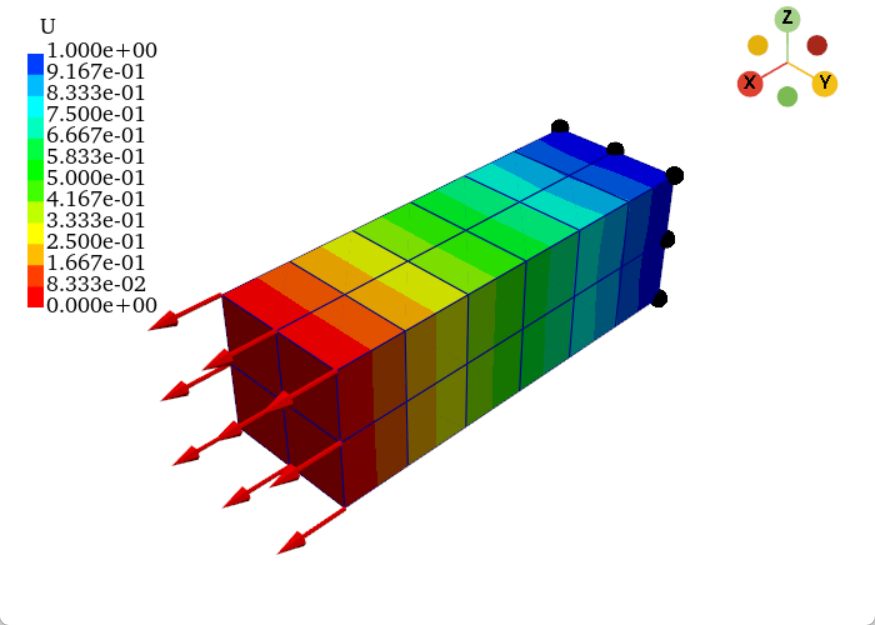
方向标志
方向标志方法有两种,代码如下,具体的参数设置我已经替大家设置完毕,看大家喜好,任选其一。
# 方向标志1
pl.add_axes(line_width=5,
cone_radius=0.6,
shaft_length=0.7,
tip_length=0.3,
ambient=0.5,
label_size=(0.4, 0.16))
# 方向标志2
pl.add_camera_orientation_widget()
大自由度模型测试
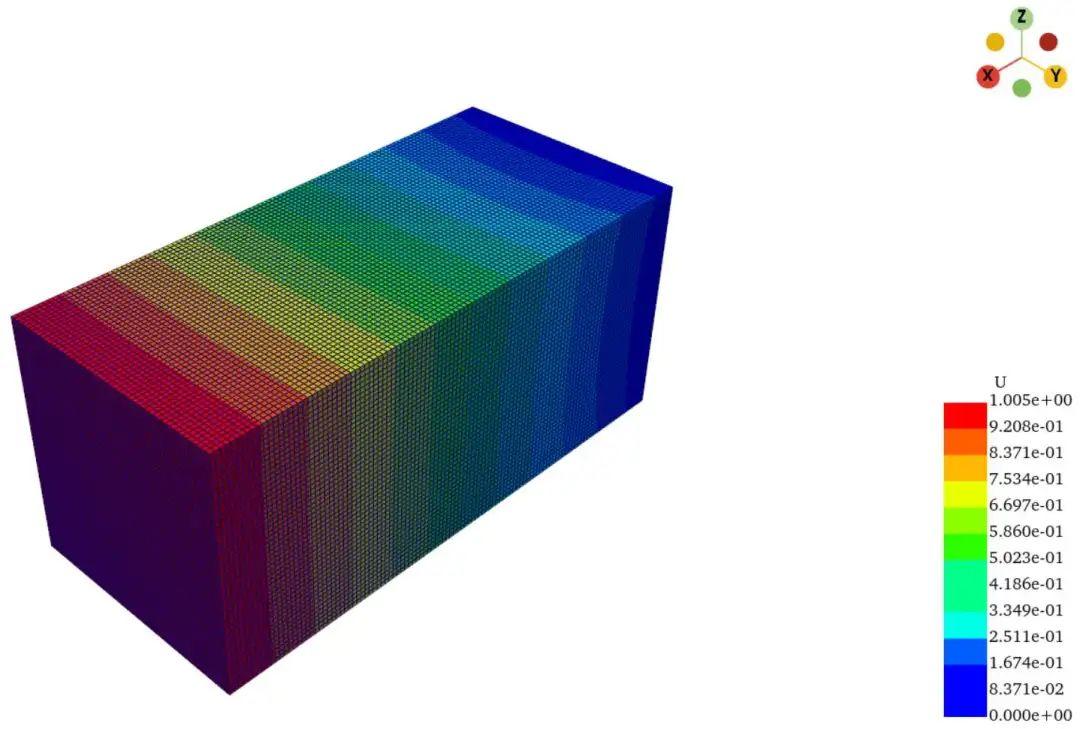
为了测试自由度较大模型的后处理显示流畅度,我以296514个节点,282500个C3D8单元模型为例。程序读取vtk文件时间为3.52秒,云图绘制时间0.02秒,是不是相当快!
# -*- coding: UTF-8 -*-
from pyvista import examples
import numpy as np
import pyvista as pv
from pyvista import themes
import time
from matplotlib.colors import LinearSegmentedColormap
# Customized drawing templates
colors = [
[0, 0, 255], [0, 93, 255], [0, 185, 255], [0, 255, 232],
[0, 255, 139], [0, 255, 46], [46, 255, 0], [139, 255, 0],
[232, 255, 0], [255, 185, 0], [255, 93, 0], [255, 0, 0]
]
colors = np.array(colors)/255.0
custom_cmap = LinearSegmentedColormap.from_list('custom_cmap', colors, N=12)
my_theme = pv.plotting.themes.DocumentTheme()
my_theme.cmap = custom_cmap
# my_theme.cmap = 'jet'
my_theme.show_edges = True
my_theme.edge_color='#000080'
my_theme.line_width=1
my_theme.render_points_as_spheres=True
my_theme.background = 'white'
my_theme.opacity=1
my_theme.nan_color = 'darkgray'
my_theme.window_size = [600, 400]
my_theme.font.family = 'times'
my_theme.title = 'FEA Result'
my_theme.show_scalar_bar=False
pv.global_theme.load_theme(my_theme)
# Testing the time to read a .vtk file
data_start_time = time.time()
mesh = pv.read('output_C3D8.vtk')
data_end_time = time.time()
dargs = dict(
scalars="Displacements",
)
pl = pv.Plotter()
# Testing the time to plot
plot_start_time = time.time()
pl.add_mesh(mesh.copy(), **dargs)
pl.add_scalar_bar(title="U",n_labels=13,n_colors=12,fmt='%.3e',vertical=True)
pl.add_camera_orientation_widget()
plot_end_time = time.time()
pl.show()
print("read .vtk file time: ", data_end_time - data_start_time, "s")
print("plot time: ", plot_end_time - plot_start_time, "s")
篇幅有限,其他绘图功能请详查:
https://docs.pyvista.org/version/stable/api/


