露天转地下采场覆岩采动裂隙演化特征
论文题目
2.Key Laboratory of Rock Mechanics and Geohazards of Zhejiang Province, Shaoxing University, Shaoxing 312000, China
3.College of Civil Engineering, Qilu Institute of Technology, Jinan 250200, China
4.State Key Laboratory of Safety and Health for Metal Mines, Maanshan 243000, China
5.School of Resources and Environmental Engineering, Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, Ganzhou 341000, China
6.School of Resources and Safety Engineering, Chongqing University, Chongqing 400044, China
研究内容
Abstract: The mechanical properties and engineering response characteristics of rock under the interaction of slope rock mass and underground mining have always been a major difculty in research. In this paper, the deep ore body of No. 2 pit of Jinning Phosphate Mine was taken as the engineering background. In order to reveal the deformation and failure process and evolution laws of fractured rock masses, semi-quantitative indicators such as the shape, quantity, density, size, distribution range, spatial position, and rock mass movement angle of the developed fssures were analyzed. In addition, the morphological equation of the outermost fracture zone of the slope, the surrounding rock of the underground stope, and the overlying rock mass was established after the open-pit was converted to the underground. Combined with the physical model experiments (model slope height was 200 m; slope angle was 55°), MatDEM numerical simulation showed that (1) after the pillar mining was completed, the fssures at the left and right ends of the overlying rock mass were mostly long fssures with medium and high angles (30° ~ 90°), while the middle part and near the main fssures were mostly small fssures with low angles (0°~30°). (2) The fracture evolution of the overlying rock mass in the mining area was a dynamic stratifcation process that extends upward in turn, accompanied by shedding, falling, and collapse. This study can provide theoretical guidance for the safe and efective mining of gently inclined phosphate rock.
Keywords: Open-pit to underground · Mining fssures · Similar simulation experiment · Mathematical statistics methods · MatDEM numerical simulation

Fig. 2 Engineering background. a Geographical location of Yunnan Province. b Geographical location of the mining area. c Open-pit mining fssures

Fig. 4 Similar material physical model
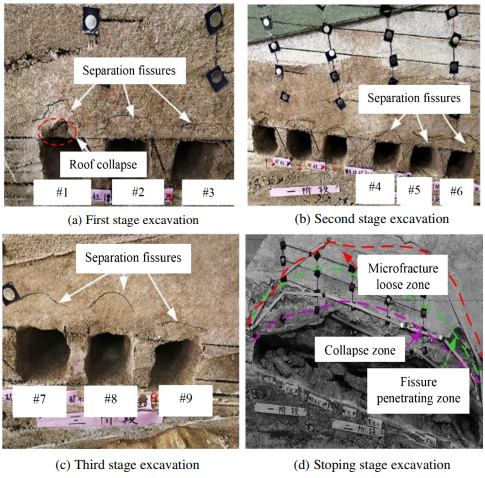
Fig. 7 Fracture development characteristics of underground stopes in diferent excavation stages. a First stage excavation. b Second stage excavation. cThird stage excavation. d Stoping stage excavatio
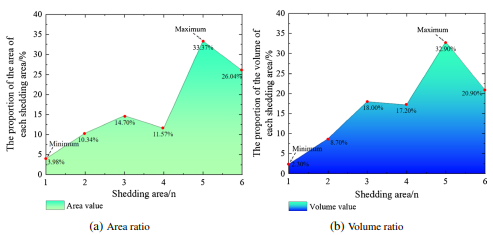
Fig. 13 Calculation of the area and volume of the shedding region above each pillar. a Area ratio. b Volume ratio
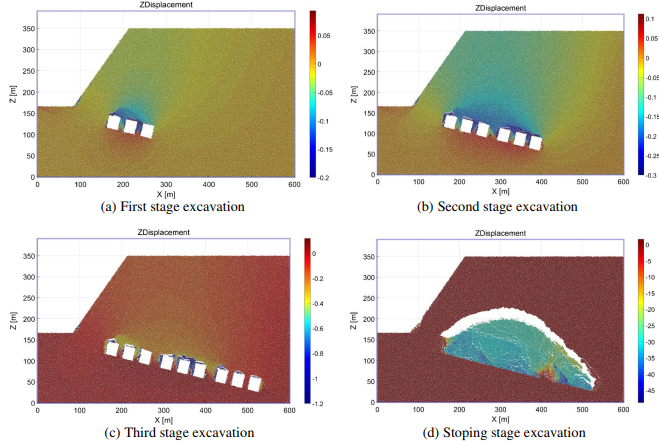
Fig. 16 Displacement distribution of rock mass in diferent stages of mining. a First stage excavation. b Second stage excavation. c Third stage excavation. d Stoping stage excavation
了解详情
Li X, Li Q, Hu Y, et al. Evolution characteristics of mining fissures in
overlying strata of stope after converting from open-pit to underground[J].Arabian Journal of Geosciences, 2021, 14(24): 1-18.




