基于离散断裂网络(DFN)的边坡稳定性分析
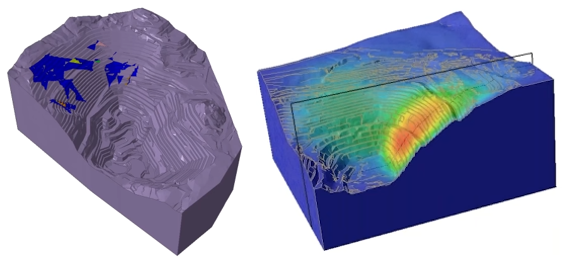
(2) Calibration of Toppling Slope Failures with Discrete Fracture Network Finite Element Modeling: A Case Study. (用离散断裂网络有限元模拟校准倾覆边坡破坏:案例研究)
(3) Implicit 3D geomechanical modeling and numerical analysis for open pit structures with hypothetical failure studies.(露天矿隐式三维地质力学模拟和数值分析)
(4) Numerical Modelling of Fault Structures and Anisotropy – Just How Different Can the Answer Be? (断层和各向异性的数值模拟 - 结果会有多大的差异?)
(5) Synthetic Rock Mass Modeling of Progressive Unravelling And Overall Slope Stability Using The Discrete Element Method. (使用离散元法对边坡稳定性进行合成岩体模拟)

(1) Probabilistic Bench Scale Slope Designs Based Upon Realistic Discrete Fracture Network Models. (基于真实离散断裂网络模型的概率性台阶尺度边坡设计)
(2) DFN based analysis of step path failure pathways for improved slope stability analysis. (基于离散断裂网络的阶梯路径破坏路径分析以提高边坡稳定性分析)
(3) DFN models were used to analyze potential failure mechanisms along discontinuity networks. (离散断裂网络模型用于分析沿着不连续网络的潜在破坏机制)
(4) Advanced Strength Reduction Search Strategies Applied to Finite Element Analysis of Slope Stability. (应用于边坡稳定性有限元分析的先进强度折减搜索策略)
(5) DFN models were integrated with finite element strength reduction analysis. (离散断裂网络模型与有限元强度折减分析的集成)
(6) Definition of intact rock bridges for 2D and 3D slope stability problems. (
为二维和三维边坡稳定问题定义完整的岩桥)
(7) Probabilistic stability analysis of slopes in highly heterogeneous rock masses. (对高度非均质岩体边坡的概率稳定性分析)
(8) DFN models were utilized for the probabilistic assessment of stability in jointed rock slopes. (利用离散断裂网络模型对节理岩石边坡稳定性进行概率评估)
4. DFN的优点和缺点




