全网最完整!LS-DYNA接触类型简介!
本文摘要(由AI生成):
本文主要介绍了LS-DYNA的接触类型,包括14个大类,其中OPTION1的可选种类非常多,体现了LS-DYNA具有非常丰富的接触类型。此外,文章还介绍了一些其他类型的接触,如将佩戴模型与接触界面相关联、自动移动主面以闭合从面和主面之间的未指定间隙、定义接触实体、定义GEBOD假人与有限元模型的零件或节点之间的接触相互作用等。
00 背景
在ANSYS结构产品中,Mechanical提供了两种线性接触和三种非线性接触。相比之下,LS-DYNA的接触类型和接触定义要复杂很多。本文简介LS-DYNA的接触类型。
01 接触类型
选择接触类型的关键字。合计14个大类。

02 CONTACT_OPTION1

OPTION1的可选种类非常多,这也体现了LS-DYNA具有非常丰富的接触类型。可以分为子类:airbag、automatic、constraint、drawbead、eroding、forming、nodes、one_way、rigid、single、sliding、spotweld、surface、tiebreak、tied。






03 其它接触类型

Purpose: Associate a wear model to a contact interface.
用途:将佩戴模型与接触界面相关联。

Purpose: This feature allows for automatic move of a master surface in a contact definition to close an unspecified gap between a slave and the master surface. The gap may be caused as a result of an initial gravity loading on the slave part. The gap will be closed on a specified time to save CPU time. The master surface in metal forming application will typically be the upper cavity and the slave part will be the blank. This feature is applicable only for sheet metal forming application.
用途:该特征允许在接触定义中自动移动主面,以闭合从面和主面之间的未指定间隙。该间隙可能是由于从动部件上的初始重力载荷而引起的。间隙将在指定的时间内闭合,以节省CPU时间。金属成型应用中的主面通常是上模腔,从零件通常是毛坯。此功能仅适用于钣金成型应用。

Purpose: Define a coupling surface for MADYMO to couple LS-DYNA with deformable and rigid parts within MADYMO. In this interface, MADYMO computes the contact forces acting on the coupling surface, and LS-DYNA uses these forces in the update of the motion of the coupling surface for the next time step. Contact coupling can be used with other coupling options in LS-DYNA.
用途:为MADYMO定义一个耦合面,将LS-DYNA与MADYMO内的可变形和刚性零件耦合。在该界面中,MADYMO计算作用在耦合面上的接触力,LS-DYNA在下一时间步的耦合面运动更新中使用这些力。接触耦合可以与LS-DYNA中的其他耦合选项一起使用。

Purpose: Define a contact entity. Geometric contact entities treat the impact between a deformable body, defined as a set of slave nodes or nodes in a shell part set, and a rigid body. The shape of the rigid body is determined by attaching geometric entities. Contact between these geometric entities and the slave nodes is a penalty formulation. The penalty stiffness is optionally maximized within the constraint of the Courant criterion. As an alternative, a finite element mesh made with shells can be used as geometric entity. Also, axisymmetric entities with arbitrary shape made with multilinear polygons are possible. The latter is particularly useful for metal forming simulations. See *DATABASE_GCEOUT for contact force output.
用途:定义接触实体。几何接触实体处理可变形体和刚体之间的碰撞,可变形体定义为从节点集或壳零件集的节点。刚体的形状是通过附着几何实体来确定的。这些几何实体和从节点之间的接触使用罚函数方法。罚刚度在Courant准则的约束范围内可选最大化。作为一种替代方案,可以使用由壳体制成的有限元网格作为几何实体。此外,用多线多边形制成的具有任意形状的轴对称实体也是可能的。后者对于金属成形模拟特别有用。有关接触力输出,请参见*DATABASE_GCEOUT。

Purpose: Create a force transducer to measure the contact force of a 3D contact. LS-DYNA only outputs data between a master and slave surface. Self-contact, such as single surface contact, only has a slave definition. In the case of self-contact, force transducers provide a means to record the self-contact forces. Force transducers are not needed for other types of contact. However, they may be useful for extracting the contact forces for any part of the model. For instance, if you have two-way contact, you may only want to extract the forces on a section of the master. Force transducers do not apply any force to the model nor do they have any effect on the solution.
用途:创建一个力传感器来测量3D接触的接触力。LS-DYNA仅在主面和从面之间输出数据。自接触,如单面接触,仅具有从定义。在自接触的情况下,力传感器提供了一种记录自接触力的方法。其他类型的接触不需要力传感器。然而,它们可能有助于提取模型任何部分的接触力。例如,如果你有双向接触,你可能只想提取一部分主体上的力。力传感器不会对模型施加任何力,也不会对结果产生任何影响。

Purpose: Define contact interaction between the segment of a GEBOD dummy and parts or nodes of the finite element model. This implementation follows that of the contact entity, however, it is specialized for the dummies. Forces may be output using the *DATABASE_GCEOUT command. See *COMPONENT_GEBOD and Appendix N for further details.
用途:定义GEBOD假人与有限元模型的零件或节点之间的接触相互作用。遵循接触实体,然而,它是专门用于假人的。可以使用*DATABASE_GCEOUT命令输出力。有关更多详细信息,请参阅*COMPONENT_GEBOD和附录N。

Purpose: Define a sliding contact that guides 1D elements, such as springs, trusses, and beams, along a path defined by a set of nodes. Only one 1D element can be in contact with any given node in the node set at a given time. If for some reason, a node is in contact with multiple 1D elements, one guided contact definition must be used for each contact. The ordering of the nodal points and 1D elements in the input is arbitrary.
用途:定义滑动接触,该滑动接触沿一组节点定义的路径引导1D单元,如弹簧、桁架和梁。在给定时间,只有一个1D单元可以与节点集中的任何给定节点接触。如果由于某种原因,一个节点与多个1D单元接触,则必须为每个接触使用一个引导接触定义。节点和1D单元的排序是任意的。

Purpose: Define interior contact for solid elements. Frequently, when soft materials are compressed under high pressure, the solid elements used to discretize these materials may invert leading to negative volumes and error terminations. To keep these elements from inverting, it is possible to consider interior contacts between layers of interior surfaces made up of the faces of the solid elements. Since these interior surfaces are generated automatically, the part (material) ID’s for the materials of interest are defined here, prior to the interface definitions.
用途:定义实体单元的内部接触。通常,当软材料在高压下被压缩时,用于离散这些材料的实体单元可能会反转,从而导致负体积和误差终止。为了防止这些单元反转,可以考虑由实体单元表面组成的内表面层之间的内部接触。由于这些内表面是自动生成的,因此在界面定义之前,此处定义感兴趣材料的零件(材料)ID。

Purpose: Define rigid surface contact. The purpose of rigid surface contact is to model large rigid surfaces, e.g., road surfaces, with nodal points and segments that require little storage and are written out at the beginning of the binary databases. The rigid surface motion, which can be optionally prescribed, is defined by a displacement vector which is written with each output state. The nodal points defining the rigid surface must be defined in the *NODE_RIGID_SURFACE section of this manual. These rigid nodal points do not contribute degrees-of-freedom.
用途:定义刚性面接触。刚性面接触的目的是对大型刚性面进行建模,例如道路表面,其节点占用存储很少,并且在二进制数据库的开头就写出来了。刚性面运动可以任意规定,由位移矢量定义,该位移矢量与每个输出状态一起写入。定义刚性面的节点必须在本手册的*NODE_rigid_surface部分中定义。这些刚性节点不贡献自由度。

Purpose: Define contact between SPG particles from different SPG parts or self-contact of SPG particles from the same SPG part. This keyword was developed for high-speed deformations, such as projectile impact penetration problems.
用途:定义不同SPG零件的SPG颗粒之间的接触或同一SPG零件的SPG颗粒的自接触。这个关键词是针对高速变形而开发的,例如炮弹冲击穿透问题。

Purpose: Define one-dimensional slide lines for rebar in concrete.
用途:为混凝土中的钢筋定义一维滑移线。
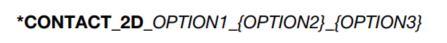
Purpose: Define a two-dimensional contact interface or slide line. This option is to be used with two-dimensional solid and shell elements using the plane stress, plane strain or axisymmetric formulations; see *SECTION_SHELL and *SECTION_BEAM.
用途:定义二维接触界面或滑移线。该选项用于平面应力、平面应变或轴对称的二维实体和壳单元;请参阅*SECTION_SHELL和*SECTION_BEAM。
04 总结
LS-DYNA提供了非常丰富的接触类型。尤其CONTACT_OPTION下还可以分为更多的子类型,每种类型的接触又会涉及各种接触属性定义。总体来说,LS-DYNA的接触类型和接触定义是极其复杂和丰富的。
南京迈力特力数字科技有限公司,专注于工程仿真的培训和咨询。能够高效提升学员的仿真技术,专业解决客户的工业问题。
公司集结国内工业产品专家和工程仿真专家数十人,具有深厚的工业背景,丰富的工程经验,熟练的软件技能,扎实的理论基础。





