PFC休止角(堆积角)计算的滚筒方法——砂土颗粒
本文摘要(由AI生成):
本文介绍了休止角的计算方法,包括自然下落法和滚筒法。自然下落法受颗粒数目限制且随机性大,而滚筒法在低颗粒数目下也能得到较好的模拟效果。文章通过砂土颗粒的滚筒模拟,详细描述了模拟过程所需的代码,并解释了模拟中需要注意的摩擦效率和滚动速度等因素。最后,通过量角器或图像处理方法,可以从模拟结果中得到休止角。未来还将探索不规则块体和稻谷颗粒的滚筒模拟。

休止角的计算常用的有自然下落,然是这个方法受限制于颗粒数目,而且随机性较大。
而滚筒法在低颗粒数目情况下也能有比较好的模拟效果。
这里给出砂土颗粒的滚筒模拟结果。
首先在生成圆形容器并且生成颗粒,加重力平衡
new
domain extent -1 1
wall generate circle position 0 0 radius 1
ball distribute porosity 0.28 radius 0.006 0.009 range annulus center 0 0 radius 0 [1-0.009]...
plane o 0 0 dip 0 belowcmat default model linear method deformability emod 100e6 kratio 1.74 property fric 0.5
ball attribute density 2.7e3 damp 0.7
cycle 2000 calm 50
set gravity 9.8
solve
save sample
以上为得到初始状态所需的代码。
然后简单的给圆形容器一个滚动速度便可以了,注意墙和球之间的摩擦效率要很大,这样模拟效率高。
ball attribute displacement multiply 0
cmat add model linear method deformability emod 100e6 kratio 1.74 property fric 1.5 range contact type ball-facet
[time_record=2]
set mech age 0
[time_record=mech.age]
def savefile
if mech.age-time_record > baocunpinlv then
filename=string.build("jieguo%1",count)
command
save @filename
endcommand
time_record=mech.age
count +=1
endif
endwall attribute centrotation 0 0 spin 50
solve time 50
50s效果不够的话,可以继续运行最后一句话。
最后颗粒表面会稳定在某一个角度,这个角度就是休止角。简单用量角器量,或者用图像处理方法得到表面轮廓,进行线性拟合,都可以得到这个角度。
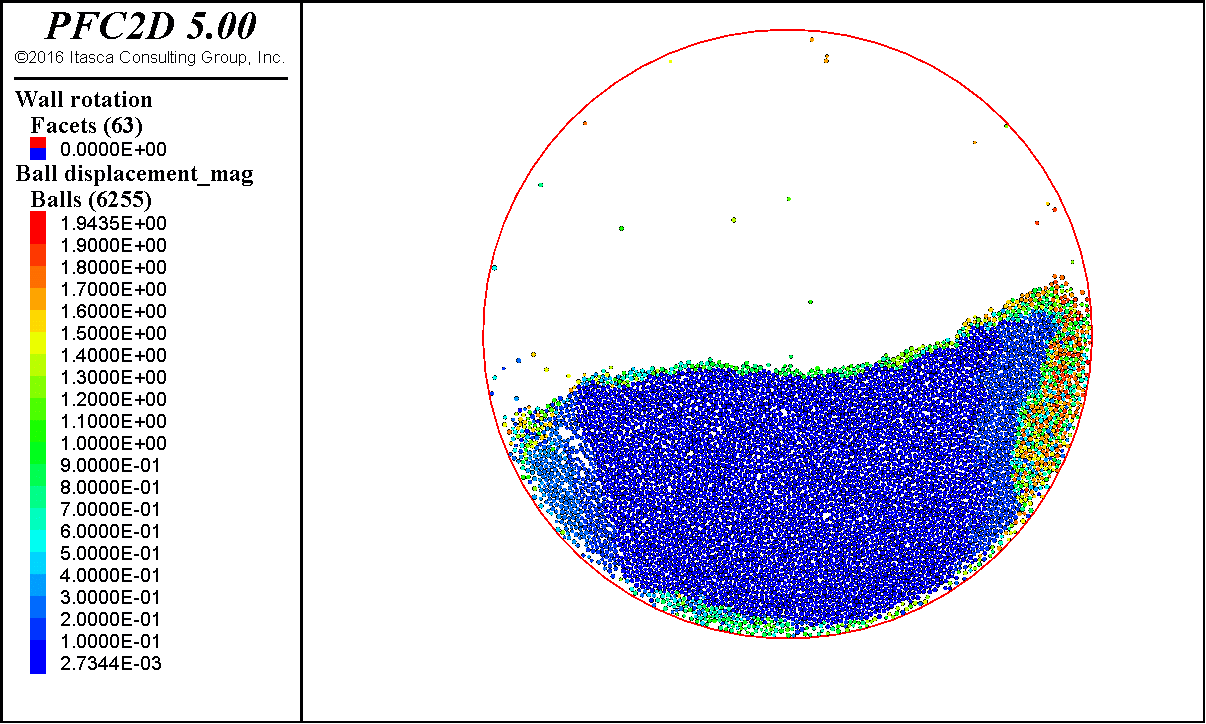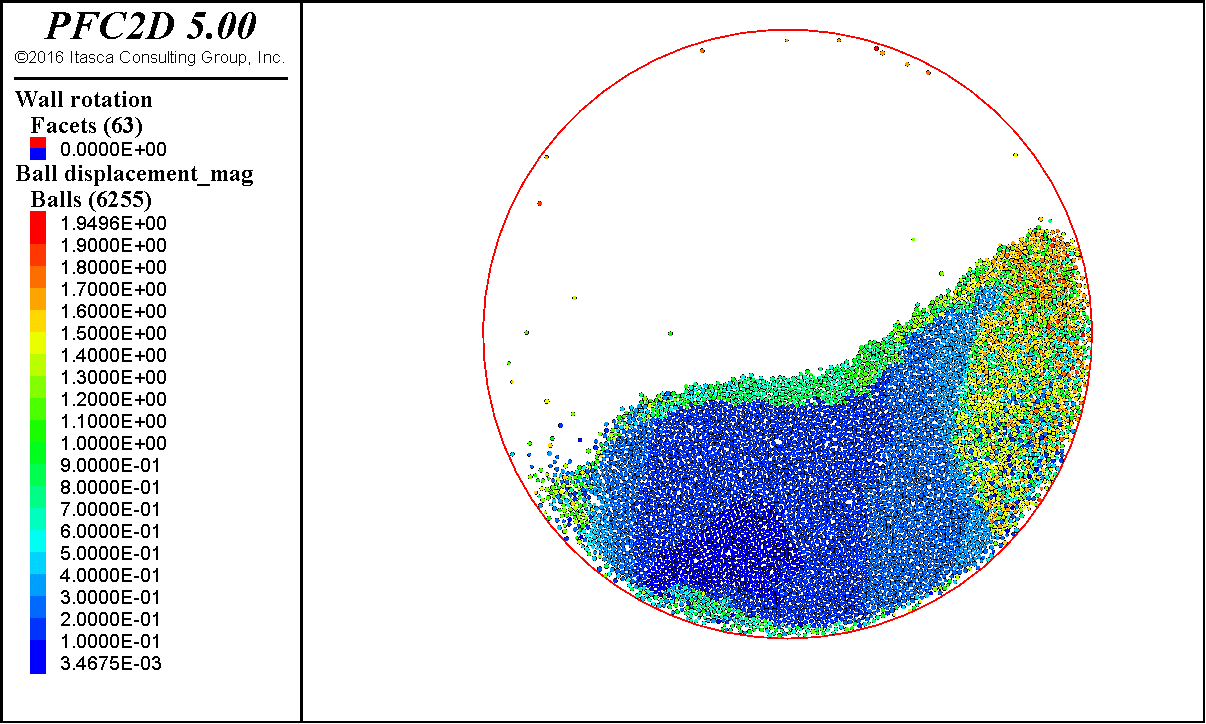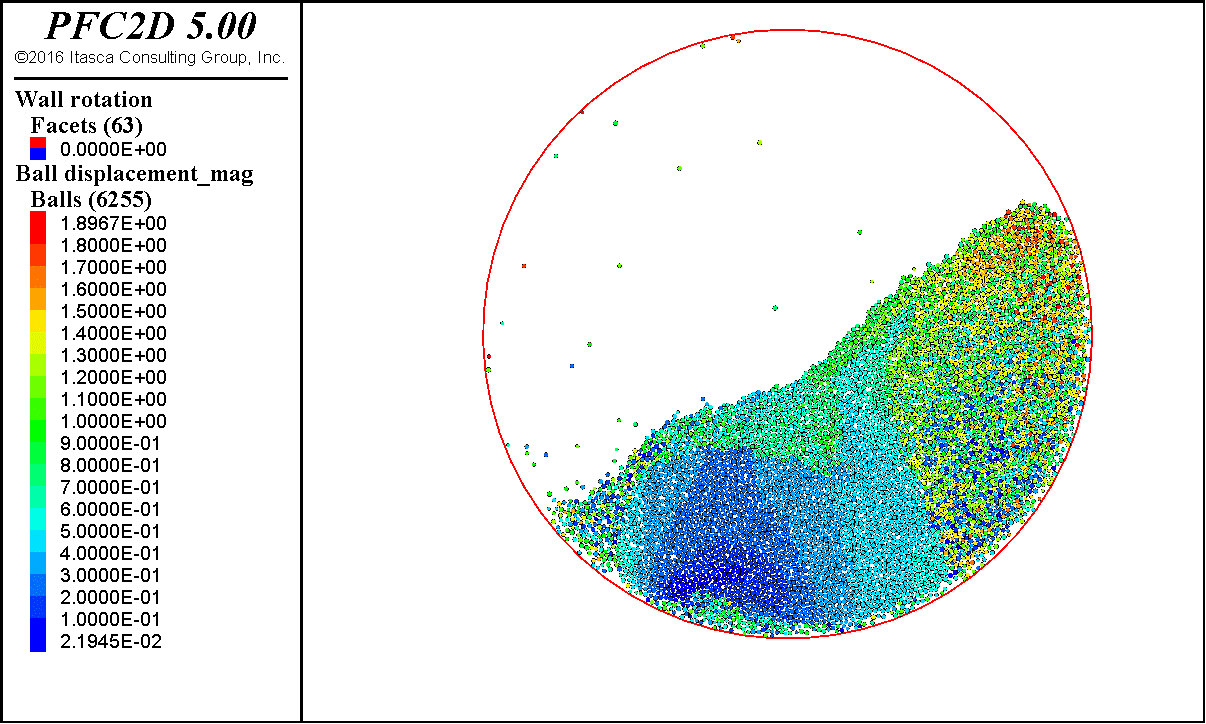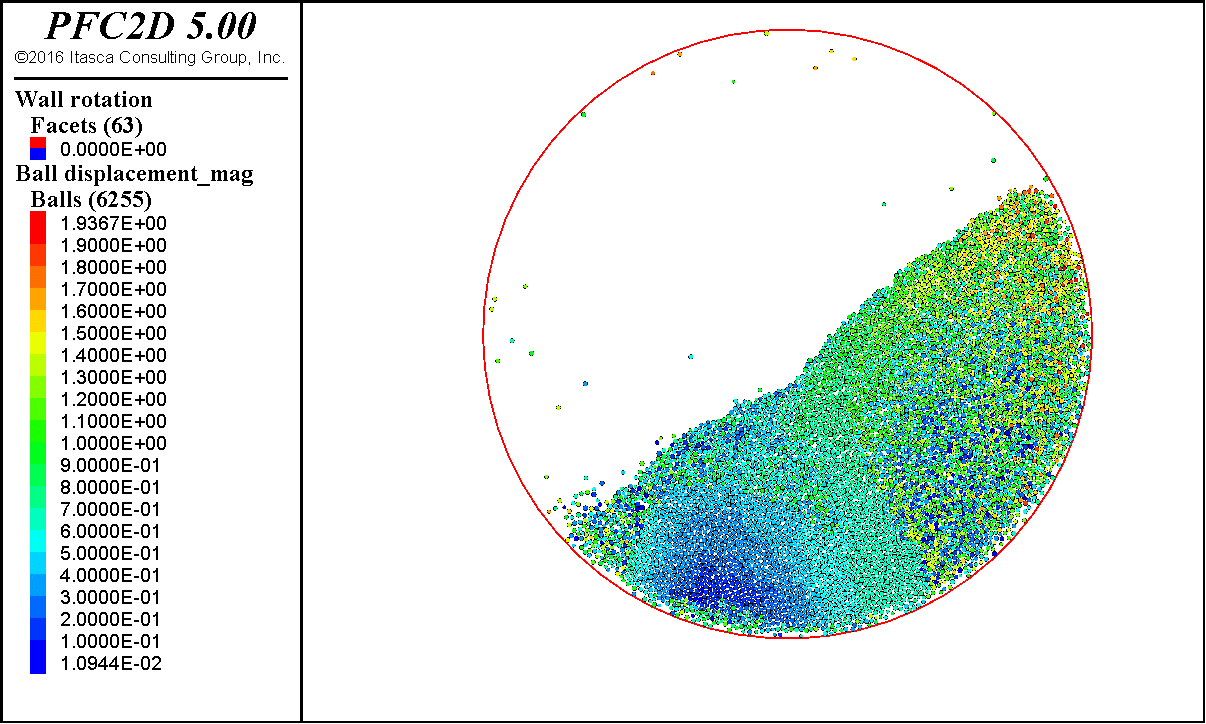
后面也会带来不规则块体和稻谷颗粒的滚筒模拟。




