STAR-CCM | 显卡散热仿真
本文利用STAR-CCM 演示显卡散热的仿真过程。
注:本案例来自STAR-CCM 官方教程。
问题描述
日常工作生活中,台式电脑及工作站的使用已经非常普遍了。我们经常能看到机箱内会有几个风扇,在电脑工作的时候,它们在不停的旋转。这些风扇的作用是加快机箱内的空气流动,帮助其中的电子元器件散热。本文主要对电脑显卡的散热问题进行仿真计算。
几何模型如下图所示。主要包括机箱、显卡、进口风扇、出口风扇等部件。
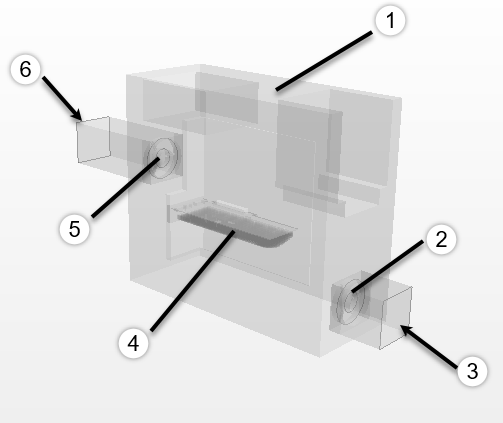 △ 几何模型
△ 几何模型
| 编号 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 1 | PC Tower Case(机箱) |
| 2 | Inlet Fan |
| 3 | Inlet |
| 4 | Graphics Card(显卡) |
| 5 | Outlet Fan |
| 6 | Outlet |
求解设置
这部分内容主要包括:区域分配、物理模型设置、网格划分以及求解器设置等内容。
区域分配
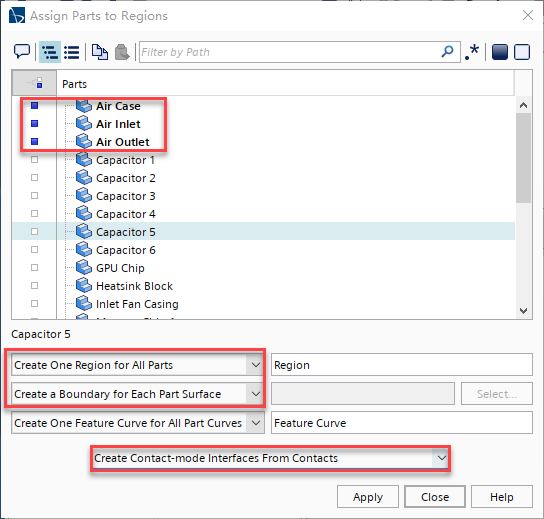
导入几何文件,选择File > Import > Import Surface Mesh,然后在Open对话框中打开文件: graphicsCardAndEnclosure.x_t;右击Geometry > Parts > Air Case节点,并选择Assign Parts to Regions; 在Assign Parts to Regions对话框中设置如下:
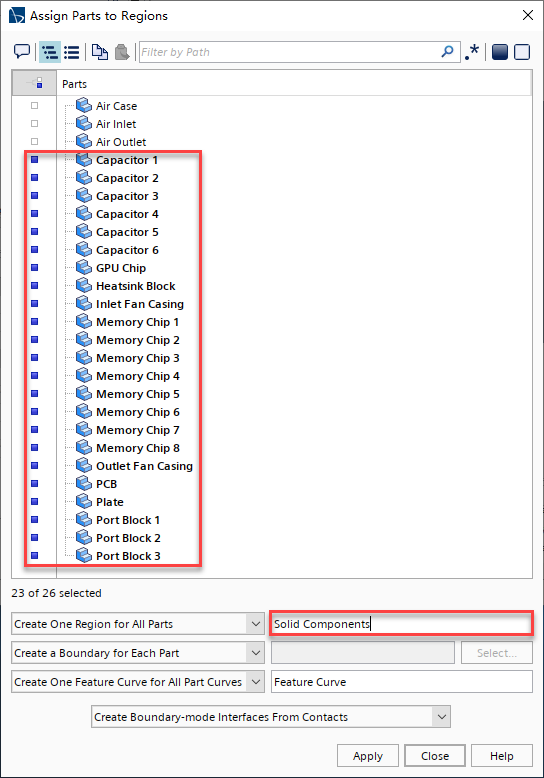
右击Geometry > Parts > GPU Chip,然后在Assign Parts to Regions对话框中设置如下图所示:
展开Interfaces节点,对交界面重命名,如下表所示:
| 旧名称 | 新名称 |
|---|---|
| Air Case/Air Inlet | Case Fans |
| Air Case/Capacitor 1 | Air/Solid Components |
| Capacitor 1/PCB | Solid Components/Solid Components |
物理模型设置
首先是固体区域的物理模型设置:
创建物理连续体Physics Continuum; 将Physics 1重命名为Solid Components; 设置物理模型如下图所示:
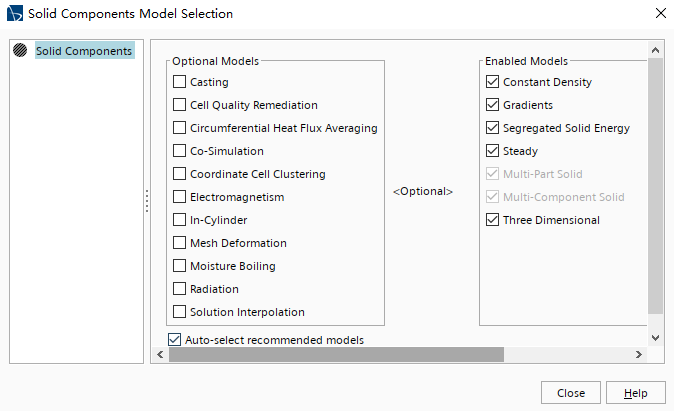 △ 固体物理属性设置
△ 固体物理属性设置
展开Continua > Solid Components > Models > Multi-Part Solid节点,右击Solids节点,然后选择Select Mixture Components; 在Select Mixture Components对话框,展开Material Databases > Standard > Solids节点; 从材料列表里面随意选四种材料,至于选什么材料不重要,因为后面会修改材料属性参数; 点击Apply然后选择Close; 重命名材料为ABS, Aluminum, Alumina, and Silicon,如下图所示:
△ 重命名材料
编辑Multi-Part Solid节点,设置材料属性如下列表格所示:
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| ABS | ||
| -Material Properties | ||
| --Density > Constant | Value | 1050 kg/m^3 |
| --Specific Heat > Constant | Value | 2050 J/kg-k |
| --Thermal Conductivity > Constant | Value | 2.5 W/m-K |
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum | ||
| -Material Properties | ||
| --Density > Constant | Value | 2700 kg/m^3 |
| --Specific Heat > Constant | Value | 896 J/kg-k |
| --Thermal Conductivity > Constant | Value | 167 W/m-K |
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| Alumina | ||
| -Material Properties | ||
| --Density > Constant | Value | 3960 kg/m^3 |
| --Specific Heat > Constant | Value | 850 J/kg-k |
| --Thermal Conductivity > Constant | Value | 30 W/m-K |
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| Silicon | ||
| -Material Properties | ||
| --Density > Constant | Value | 2330 kg/m^3 |
| --Specific Heat > Constant | Value | 700 J/kg-k |
| --Thermal Conductivity > Constant | Value | 124 W/m-K |
右击Solids节点,然后选择Select Mixture Components; 在Select Mixture Components对话框中,展开Material Databases > Standard > Solids节点,随便选一种材料,然后点击Apply,再点Close; 重命名新材料为 FR-4 Copper;展开FR-4 Copper > Material Properties节点,设置材料属性如下表所示:
| Node | Property | Setting |
|---|---|---|
| FR-4 Copper | ||
| -Material Properties | ||
| --Density > Constant | Value | 33 kg/m^3 |
| --Specific Heat > Constant | Value | 37 J/kg-k |
| --Thermal Conductivity | Method | Anisotropic |
在FR-4 Copper > Material Properties节点中,选择Thermal Conductivity > Anisotropic节点,激活Allow Legacy Method; 选择Thermal Conductivity节点,然后设置Method为Anisotropic (Legacy)。
其次是空气的物理模型设置:
创建物理连续体,并命名为Air; 设置空气的物理模型如下图所示:
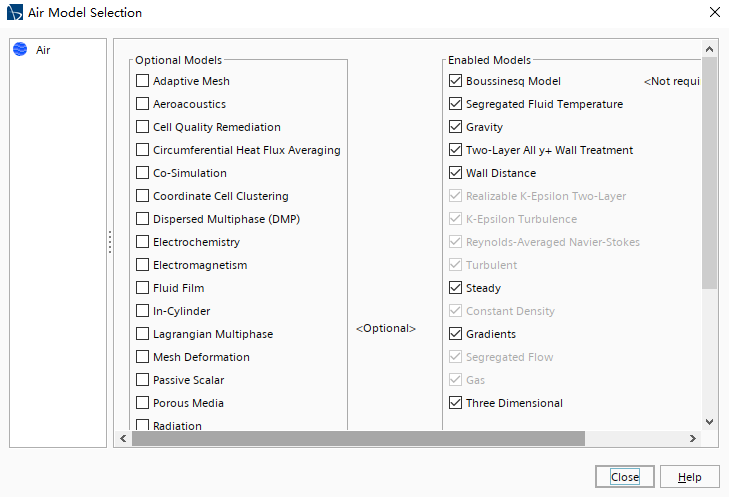 △ 空气域物理模型设置
△ 空气域物理模型设置
开启Boussinesq模型,需要设置流体域的热膨胀系数:
展开Continua > Air > Models > Gas > Air > Material Properties > Thermal Expansion Coefficient节点; 选择Constant节点,设置热膨胀系数为3.33E-3 /K; 调整重力方向,选择Continua > Air > Reference Values > Gravity节点,设置Value为[0.0, -9.81, 0.0] m/s^2。
为区域指定物理模型
因为这个问题中既有固体又有流体,所以要为固体和流体分别指定物理模型。
选择Regions > Air节点,然后设置Physics Continuum为Air; 选择Regions > Solid Components节点,然后设置Physics Continuum为Solid Components。
设置边界类型
展开Regions > Air > Boundaries节点; 选择Air Inlet.Inlet节点,设置类型为Stagnation Inlet; 选择Air Outlet.Outlet节点,设置类型为Pressure Outlet。
指定材料属性
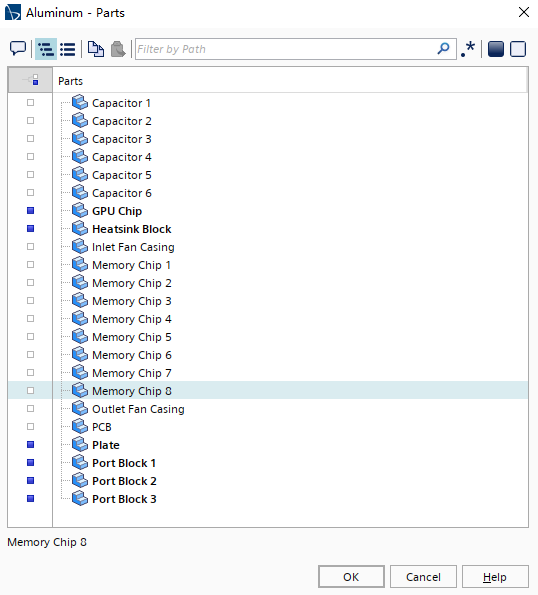
展开Regions > Solid Components > Physics Values > Material Part Groups节点; 选择Aluminum节点,并点击Custom Editor,就是属性面板Parts右边的三个点按钮; 然后在Aluminum对话框中,设置如下图所示:
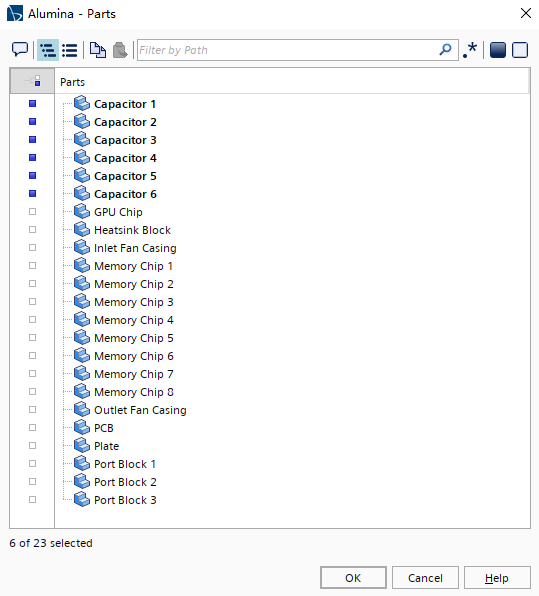
选择Alumina节点,然后设置如下图所示:
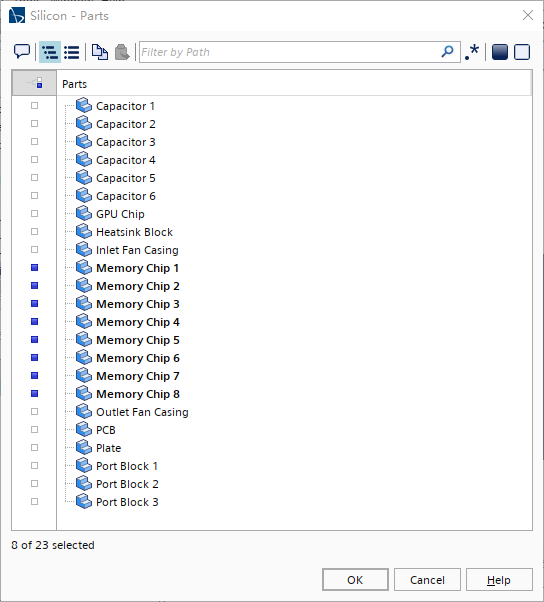
选择Silicon节点,然后设置如下图所示:
选择ABS节点,然后设置如下图所示:
选择FR-4 Copper节点,设置如下图所示:
设置热源
选择Regions > Solid Components,激活Allow Per-Part Values,此时,在Solid Components节点下会出现一个新节点Part Subgroupings; 展开Solid Components > Part Subgroupings > Subgrouping 1节点,Subgroup 1节点包含构成 Solid Components 区域的所有部件,这些部件没有分配给它们的热源; 重命名Subgroup 1为 Default;右击Subgrouping 1节点,然后选择New,会出现一个新的节点,叫做Subgroup 1; 重命名Subgroup 1为 GPU Chip;选择GPU Chip,然后将GPU Chip边界添加到Objects列表中,具体如下图所示:
再创建一个Subgroup,设置属性如下图所示:
| 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|
| Name | Memory Chips |
| Objects | Memory Chip 1 |
| Memory Chip 2 | |
| Memory Chip 3 | |
| Memory Chip 4 | |
| Memory Chip 5 | |
| Memory Chip 6 | |
| Memory Chip 7 | |
| Memory Chip 8 |
展开Solid Components > Physics Conditions节点; 选择Energy Source Option节点,设置Energy Source Option为Total Heat Source; 展开Solid Components > Physics Values节点; 选择Heat Source节点,设置方法为By Part Subgroup; 展开Heat Source > By Part Subgroup节点; 编辑By Part Subgroup节点,设置如下表所示:
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| Default | Value | 0.0 W |
| GPU Chip | Value | 25.0 W |
| Memory Chips | Value | 32.0 W |
设置PCB板各向异导热属性
展开Regions > Solid Components > Physics Values > Anisotropic Thermal Conductivity > FR-4 Copper > Anisotropic Thermal Conductivity节点; 编辑Principal Tensor节点,设置属性如下表所示:
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| XX Component | Value | 10 W/m-k |
| YY Component | Value | 0.5 W/m-k |
| ZZ Component | Value | 10 W/m-k |
设置风扇交界面
这里比较有意思,我们不需要散热风扇真的转起来,只需要设置风扇的P-Q曲线就行,具体步骤如下:
展开Interfaces节点; 选择Case Fans节点,并设置类型为Fan Interface; 激活Allow Per-Contact Values,此时,Case Fans节点下会出现一个新的节点Contact Subgroupings; 展开Case Fans > Contact Subgroupings > Subgrouping 1节点; 重命名Subgroup 1为 Inlet Fan;右击Subgrouping 1节点,选择New,新建一个Subgroup; 重命名Subgroup 1为 Outlet Fan;选择Outlet Fan,添加对象为Air Outlet/Air Case > Outlet Downstream/Outlet Upstream; 选择Case Fans > Orientation,设置模式为Manual; 右击Orientation,然后选择Reverse Contacts; 在Reverse Contacts对话框中,展开文件夹; 机箱出口出风扇的流向有问题,需要修改。选择Air Outlet/Air Case > Outlet Downstream/Oultet Upstream,然后点击OK; 选择Case Fans > Physics Conditions > Fan Curve Type节点,然后设置Curve Type为Polynomial; 展开Case Fans > Physics Values节点; 选择Fan Curve Polynomial节点,激活Specify by Part Subgroup,此时By Contact Subgroup节点就出现在了Fan Curve Polynomial中; 展开Fan Curve Polynomial > By Contact Subgroup > Inlet Fan节点; 选择Fan Curve Polynomial节点,然后点击三个点按钮; 在Fan Curve Polynomial对话框中设置如下图所示:
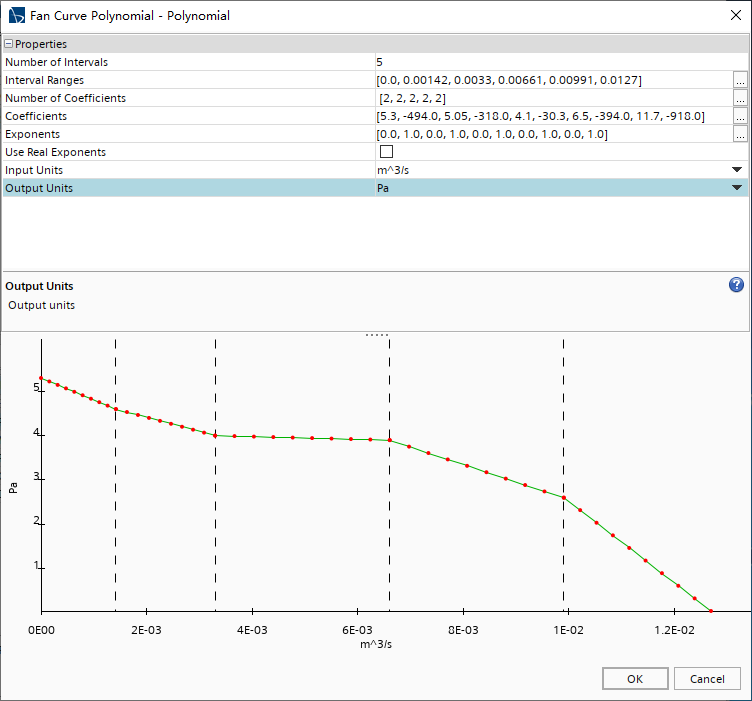
设置风扇操作转速Operating Rotation Rate为1200.0 rpm; 设置风扇性能数据对应的转速Data Rotation Rate为800.0 rpm;
进口风扇性能曲线与出口风扇相同,这里把风扇的数据从进口拷贝到出口:
右击Inlet Fan > Fan Curve Polynomial节点,选择Copy; 右击Outlet Fan > Fan Curve Polynomial节点,选择Paste;
要在界面的任一侧获得正确的热导率,就要将模拟中的所有剩余界面都设置为接触界面:
选择除风扇交界面意外的所有界面,设置类型为Contact Interface。
网格设置
右击Geometry > Operations节点,然后选择New > Mesh > Automated Mesh; 在Create Automated Mesh Operation对话框中,设置如下图,点击OK关闭窗口;
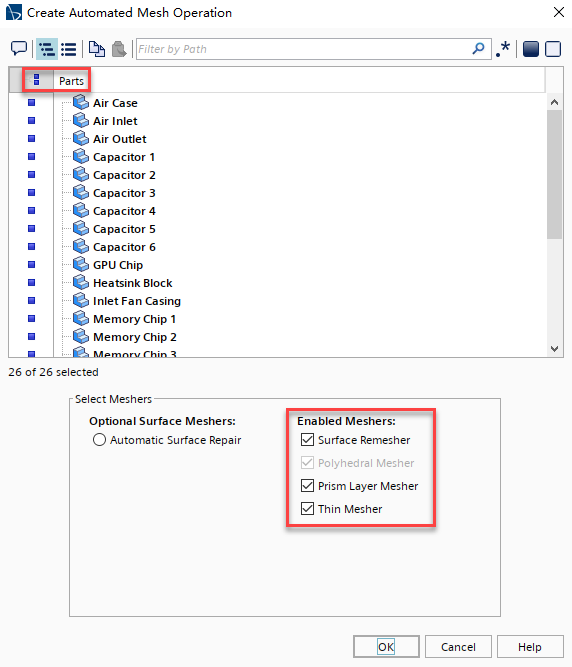
展开Automated Mesh > Meshers节点; 选择Surface Remesher节点,激活Perform Compatibility Refinement选项; 编辑Operations > Automated Mesh > Default Controls > Core Mesh Optimization节点,设置参数如下表所示;
| 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|
| Optimization Cycles | 3 |
| Quality Threshold | 0.7 |
编辑Operations > Automated Mesh > Thin Mesher,设置参数如下表所示;
| 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|
| Automatic Thin/Bulk Shape Detection | 激活 |
| Optimization Cycles | 3 |
| Quality Threshold | 0.7 |
编辑Operations > Automated Mesh > Default Controls节点,设置参数如下表所示;
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| Base Size | Value | 0.02 m |
| Prism Layer Total Thickness | Percentage of Base | 30.0 |
| Volume Growth Rate | Volume Growth Rate | 1.1 |
| Maximum Tet Size | Percentage of Base | 140.0 |
自定义网格控制
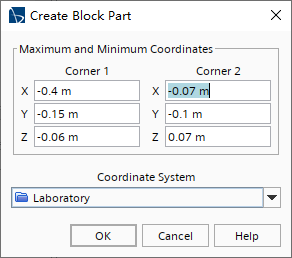
右击Geometry > Parts节点,选择New Shape Part > Block; Create/Edit Block Part对话框中,设置如下图所示,然后点击OK;
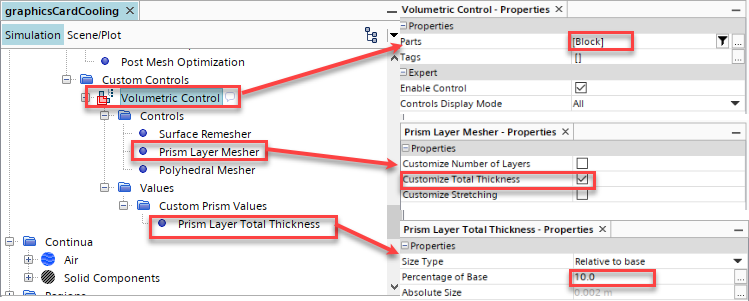
右击Operations > Automated Mesh > Custom Controls,然后选New > Volumetric Control; 编辑Volumetric Control节点,设置如下图所示;
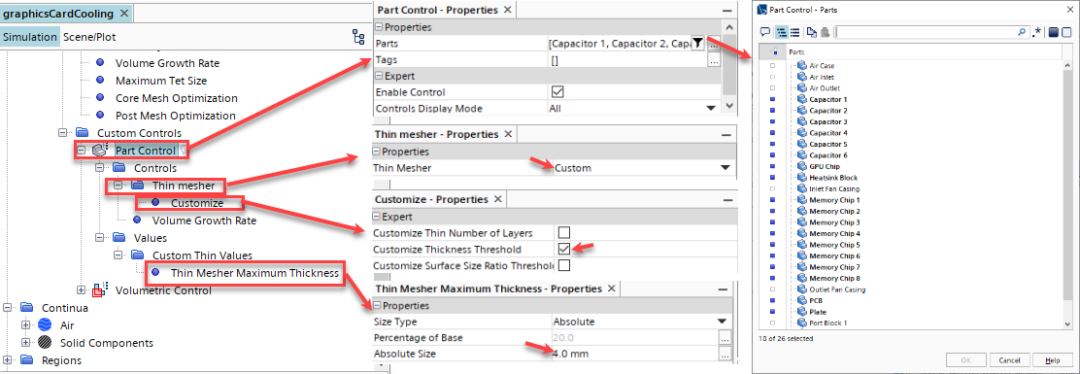
右击Custom Controls,然后选择New > Part Control; 编辑Part Control节点,然后设置如下图所示;
右击Custom Controls,选择New > Surface Control; 编辑Surface Control节点,然后设置如下图所示;
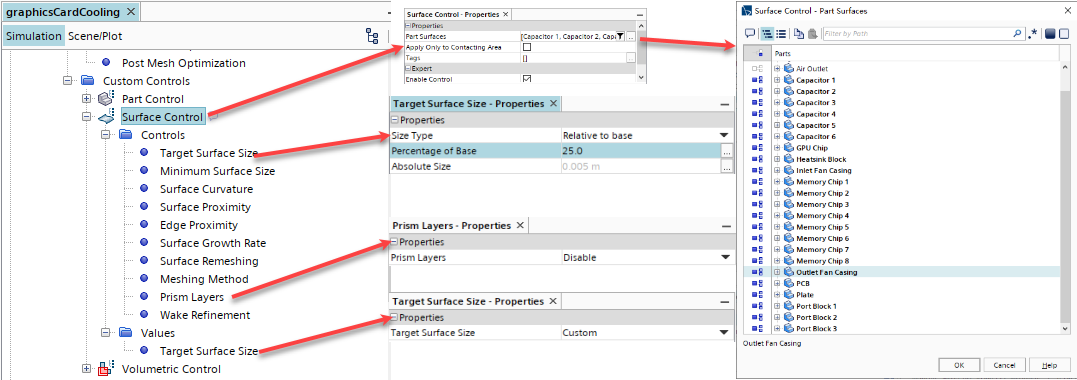
在Mesh工具条中点击Generate Volume Mesh,生成体网格,网格划分完成后如下图所示。
求解器设置
编辑Solvers节点,设置参数如下表所示;
| 节点 | 属性 | 设置 |
|---|---|---|
| Segregated Energy | Fluid Under-Relaxation Factor | 0.99 |
| Solid Under-Relaxation Factor | 0.9999 |
选择Stopping Criteria > Maximum Steps节点,设置最大迭代步数为500; 在 Solution工具条中点击Run。
分析结果
机箱内速度云图:
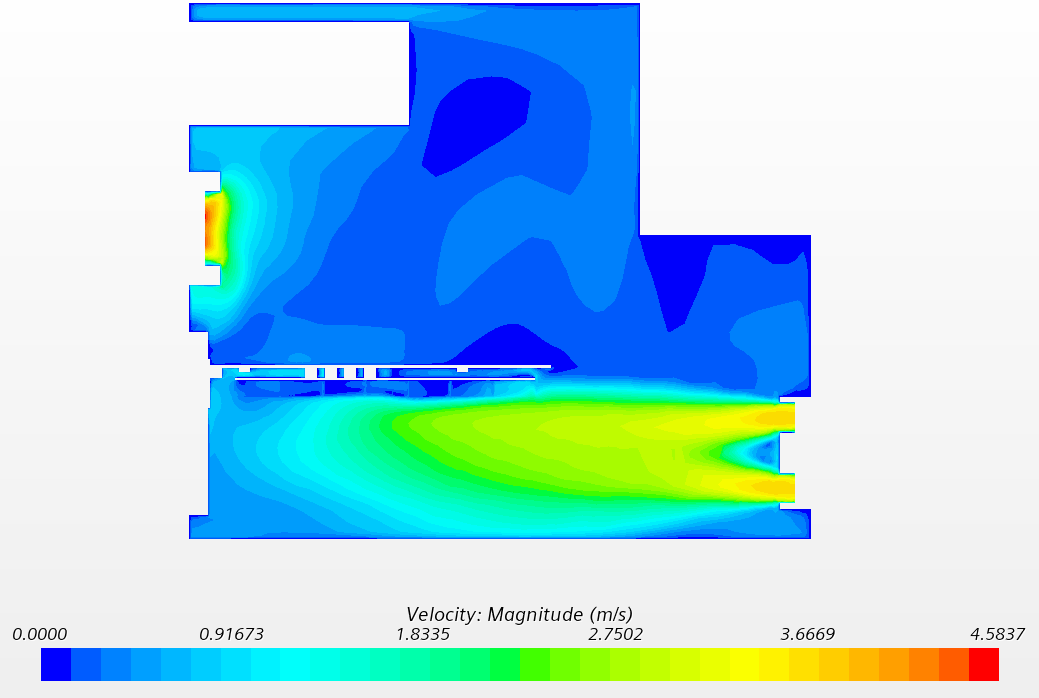 △ 机箱内速度云图
△ 机箱内速度云图
机箱最大温度监测:
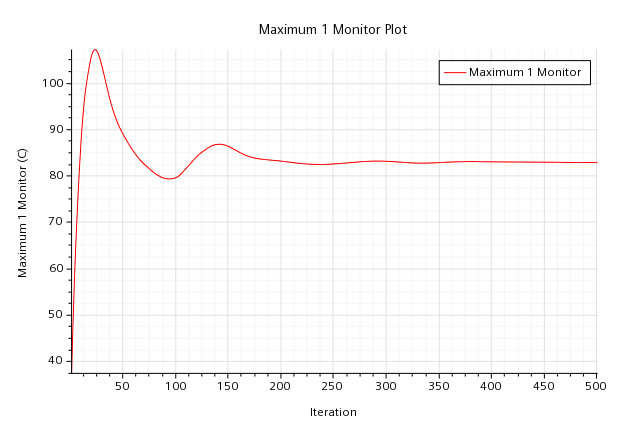
显卡温度云图:
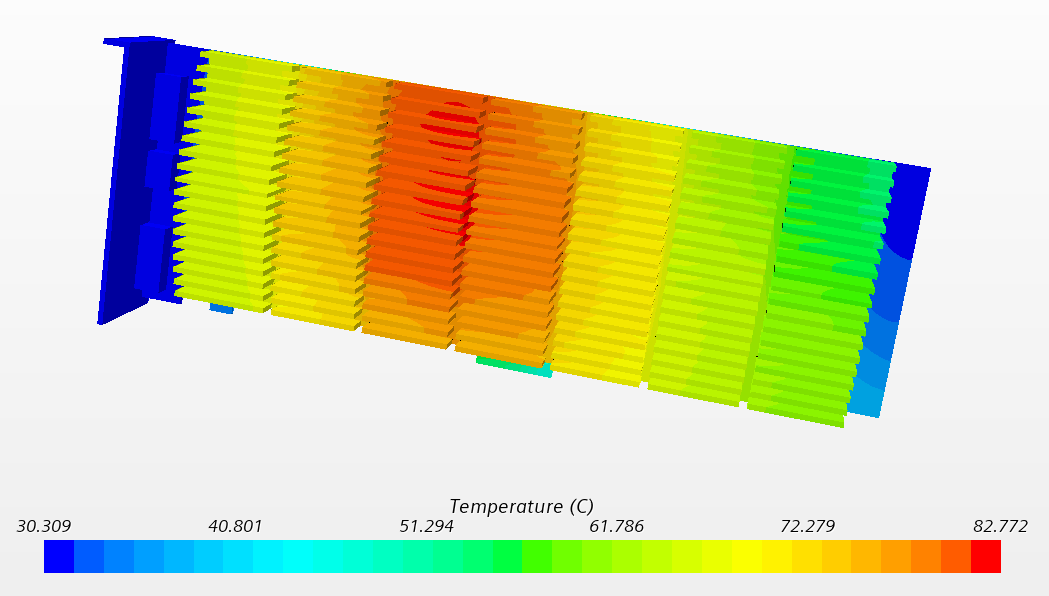 △ 显卡温度云图
△ 显卡温度云图
以上就是本文的全部内容,感谢您点个大大的赞,我们下期再见!
登录后免费查看全文
附件
著作权归作者所有,欢迎分享,未经许可,不得转载
首次发布时间:2022-03-30
最近编辑:2年前
作者推荐
相关推荐
最新文章






