OpenFOAM|22 自定义初始值
文章亮点
- 作者优秀
- 优秀教师/意见领袖/博士学历/特邀专家
- 平台推荐
- 内容稀缺
本文描述利用codeStream与setField自定义初始条件。
1 介绍
在设置计算域的局部初始条件时,可以使用程序setFields。此实用程序非常灵活,除了可以设置指定区域内的初始值外,还可以读取STL文件并使用它们来初始化物理场。然而如果使用setFields无法获得所要的结果时,可以使用codeStream编制程序来实现自定义的初始条件。
codeStream定义初始条件与定义边界条件的方式类似,定义完毕后,在求解器求解计算时会自动编译生成程序库并加载运行。如下示例为初始化示例:
// internalField为初始条件关键字
internalField #codeStream
{
{
// 这里列举编译所需的头文件
codeInclude
#{
#include "fvCFD.H"
#};
// 这里列举编译选项
codeOptions
#{
- I$(LIB_SRC) / finiteVolume / lnInclude - I$(LIB_SRC) / meshTools / lnInclude
#};
// 这里列举编译所需的外部库
codeLibs
#{
- lmeshTools - lfiniteVolume
#};
// 这里放置功能实现源代码
code
#{
#};
};
}
如下面的示例模型。

利用codeStream定义椭圆区域内相Phase2的体积分数。可以在字典文件alpha.phase1中采用下面的代码:
internalField #codeStream
{
{
codeInclude
#{
#include "fvCFD.H"
#};
codeOptions
#{
-I$(LIB_SRC) / finiteVolume / lnInclude \
-I$(LIB_SRC) / meshTools / lnInclude
#};
codeLibs
#{
-lmeshTools - lfiniteVolume
#};
code
#{
// 访问到计算网格信息
const IOdictionary& d = static_cast<const IOdictionary&>(dict);
const fvMesh& mesh = refCast<const fvMesh>(d.db());
// 定义区域内初始体积分数为0
scalarField alpha(mesh.nCells(), 0.);
scalar he = 0.5;
scalar ke = 0.5;
scalar ae = 0.3;
scalar be = 0.15;
forAll(alpha, i)
{
// 获取网格面的x,y,z坐标
const scalar x = mesh.C()[i][0];
const scalar y = mesh.C()[i][1];
const scalar z = mesh.C()[i][2];
// 得到椭圆形区域
if ( pow(y-ke,2) <= ((1 - pow(x-he,2)/pow(ae,2) )*pow(be,2)) )
{
// 指定区域内体积分数为1
alpha[i] = 1.;
}
}
writeEntry(os, "", alpha);
#};
};
}
相同的模型其实也可以使用setField来处理,如构建下面的几何模型。

准备下面的setFieldsDict字典:
defaultFieldValues
(
volScalarFieldValue alpha.phase1 0
);
regions
(
surfaceToCell
{
file "./geo/ellipse.stl";
outsidePoints((0.5 0.85 0));
includeInside true;
includeOutside false;
includeCut false;
fieldValues
(
volScalarFieldValue alpha.phase1 1
);
}
);
2 示例
2.1示例1
如下面用于计算Rayleigh-Taylor不稳定线性的模型。

需要初始化相间界面,这里指定其相间界面为余弦函数分布:

可以编制其代码为:
code
#{
const IOdictionary &d = static_cast<const IOdictionary &>(dict);
const fvMesh &mesh = refCast<const fvMesh>(d.db());
scalarField alpha(mesh.nCells(), 0.);
forAll(alpha, i)
{
const scalar x = mesh.C()[i][0];
const scalar y = mesh.C()[i][1];
if (y >= -0.05 * cos(2 * constant::mathematical::pi * x))
{
alpha[i] = 1.;
}
}
writeEntry(os, "", alpha);
#};
2.2 示例2
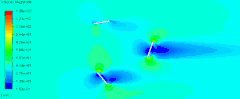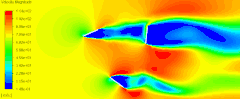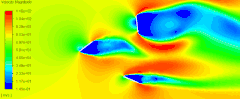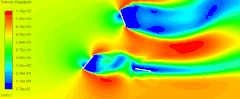
如下图所示的计算模型。

在alpha.water字典中使用codeStream指定初始水位。
internalField #codeStream
{
...
...
...
code
#{
const IOdictionary &d = static_cast<const IOdictionary &>(dict);
const fvMesh &mesh = refCast<const fvMesh>(d.db());
scalarField alpha(mesh.nCells(), 0.);
forAll(alpha, i)
{
const scalar x = mesh.C()[i][0];
const scalar y = mesh.C()[i][1];
const scalar z = mesh.C()[i][2];
if (y <= 0.2)
{
alpha[i] = 1.;
}
}
writeEntry(os, "", alpha);
#};
}
在alpha.water中指定入口边界中水相体积分数:
leftWall
{
type codedFixedValue;
value uniform 0;
name inletProfile2;
code
#{
const fvPatch &boundaryPatch = patch();
const vectorField &Cf = boundaryPatch.Cf();
scalarField &field = *this;
field = patchInternalField();
scalar min = 0.5;
scalar max = 0.7;
scalar t = this->db().time().value();
forAll(Cf, faceI)
{
if (
(Cf[faceI].z() > min) &&
(Cf[faceI].z() < max) &&
(Cf[faceI].y() > min) &&
(Cf[faceI].y() < max))
{
if (t < 2.)
{
field[faceI] = 1.;
}
else
{
field[faceI] = 0.;
}
}
}
#};
}
在0/U边界条件中指定入口速度与时间关系,使用codedFixedValue进行指定:
leftWall
{
type codedFixedValue;
value uniform(0 0 0);
name inletProfile1;
code
#{
const fvPatch &boundaryPatch = patch();
const vectorField &Cf = boundaryPatch.Cf();
vectorField &field = *this;
scalar min = 0.5;
scalar max = 0.7;
scalar t = this->db().time().value();
forAll(Cf, faceI)
{
if (
(Cf[faceI].z() > min) &&
(Cf[faceI].z() < max) &&
(Cf[faceI].y() > min) &&
(Cf[faceI].y() < max))
{
if (t < 2.)
{
field[faceI] = vector(1, 0, 0);
}
else
{
field[faceI] = vector(0, 0, 0);
}
}
}
#};
}声明:原创文章,欢迎留言与我讨论,如需转载留言
登录后免费查看全文
著作权归作者所有,欢迎分享,未经许可,不得转载
首次发布时间:2021-04-12
最近编辑:3年前
作者推荐
还没有评论
相关推荐
热门文章