OpenFOAM|算例 08 室内空气龄计算
- 作者优秀
- 优秀教师/意见领袖/博士学历/特邀专家
- 平台推荐
- 内容稀缺
本案例利用OpenFOAM中的simpleFoam求解器计算室内空间的空气龄。
注:案例位于\incompressible\simpleFoam\roomResidenceTime。
”
1 计算模型
计算模型如下图所示。计算区域内包含一个入口及一个出口,入口流速1.68 m/s,出口静压为0 Pa,计算区域达到稳态后的空气龄分布。

空气龄的计算可以直接利用functionObject来实现,并不需要修改求解器源代码。
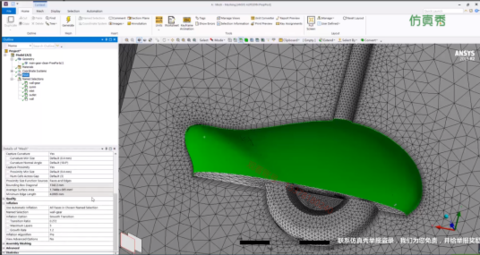
2 计算网格
本算例几何结构较为简单,直接使用blockMesh生成网格即可。网格边界包括一个入口inlet、一个出口outlet,其他边界为壁面walls。其在blockMeshDict字典中进行指定。
...
defaultPatch
{
name walls;
type wall;
}
boundary
(
inlet
{
type patch;
faces
(
(2 17 40 33)
);
}
outlet
{
type patch;
faces
(
(51 58 60 53)
);
}
);
生成的计算网格如下图所示。
2 计算模型
本算例采用kEpsilon湍流模型进行计算。在constant/momentumTransport字典文件中进行湍流模型的指定。文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "constant";
object momentumTransport;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
simulationType RAS;
RAS
{
model kEpsilon;
turbulence on;
printCoeffs on;
}
流体介质为空气,需要在字典文件constant/transportProperties文件中指定其运动粘度。文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "constant";
object transportProperties;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
transportModel Newtonian;
// Air at 23 degC
nu [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0] 1.56225e-05;
3 边界条件与初始条件
需要在0文件夹中指定初始条件与边界条件。这里需要指定文件p、U、k、epsilon、nut。
3.1 p文件
p文件如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object p;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -2 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 0;
boundaryField
{
walls
{
type zeroGradient;
}
inlet
{
type zeroGradient;
}
outlet
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform 0;
}
}
3.2 U文件
U文件如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volVectorField;
location "0";
object U;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 1 -1 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform (0 0 0);
boundaryField
{
walls
{
type noSlip;
}
inlet
{
type fixedValue;
value uniform (1.68 0 0);
}
outlet
{
type pressureInletOutletVelocity;
value uniform (0 0 0);
}
}
3.3 k文件
k文件如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object k;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -2 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 8e-2;
boundaryField
{
walls
{
type kqRWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
inlet
{
type turbulentIntensityKineticEnergyInlet;
intensity 0.14;
value $internalField;
}
outlet
{
type inletOutlet;
inletValue $internalField;
}
}
3.4 epsilon文件
epsilon文件如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object epsilon;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -3 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 0.23;
boundaryField
{
walls
{
type epsilonWallFunction;
value $internalField;
}
inlet
{
type turbulentMixingLengthDissipationRateInlet;
mixingLength 0.0168;
value $internalField;
}
outlet
{
type inletOutlet;
inletValue $internalField;
}
}
3.5 nut文件
nut文件如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class volScalarField;
location "0";
object nut;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
dimensions [0 2 -1 0 0 0 0];
internalField uniform 0;
boundaryField
{
walls
{
type nutkWallFunction;
value uniform 0;
}
inlet
{
type calculated;
value uniform 0;
}
outlet
{
type calculated;
value uniform 0;
}
}
4 计算参数文件
计算参数文件位于system文件夹。
4.1 controlDict文件
controlDict文件内容如下所示。
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object controlDict;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
application simpleFoam;
startFrom startTime;
startTime 0;
stopAt endTime;
endTime 2000;
deltaT 1;
writeControl timeStep;
writeInterval 250;
purgeWrite 0;
writeFormat ascii;
writePrecision 6;
writeCompression off;
timeFormat general;
timePrecision 6;
runTimeModifiable true;
functions
{
#includeFunc residuals
}
4.2 fvSchemes文件
文件内容:
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object fvSchemes;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * //
ddtSchemes
{
default steadyState;
}
gradSchemes
{
default Gauss linear;
}
divSchemes
{
default none;
div(phi,U) bounded Gauss upwind;
div(phi,k) bounded Gauss upwind;
div(phi,epsilon) bounded Gauss upwind;
div((nuEff*dev2(T(grad(U))))) Gauss linear;
div(phi,age) bounded Gauss upwind;
}
laplacianSchemes
{
default Gauss linear orthogonal;
}
interpolationSchemes
{
default linear;
}
snGradSchemes
{
default orthogonal;
}
wallDist
{
method meshWave;
}
4.3 fvSolution文件
文件内容:
FoamFile
{
version 2.0;
format ascii;
class dictionary;
location "system";
object fvSolution;
}
// * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * //
solvers
{
p
{
solver GAMG;
tolerance 1e-08;
relTol 0.1;
smoother GaussSeidel;
}
"(U|k|epsilon)"
{
solver PBiCG;
preconditioner DILU;
tolerance 1e-08;
relTol 0.1;
}
// 这里添加了age方程的求解算法
age
{
$U;
relTol 0.001;
}
}
SIMPLE
{
consistent yes;
residualControl
{
p 1e-3;
U 1e-4;
"(k|epsilon)" 1e-4;
}
}
relaxationFactors
{
fields
{
p 1;
}
equations
{
U 0.95;
k 0.7;
epsilon 0.7;
age 1;
}
}
5 求解计算
先执行simleFoam进行流场计算,终端中执行命令:
simpleFoam
5.1 计算age
准备age计算的functionObject字典。可以在system文件夹下新建一个字典文件,如命名为age,其内容如下所示:
type age;
libs ("libfieldFunctionObjects.so");
diffusion true;
executeControl writeTime;
writeControl writeTime;
运行下面的命令:
simpleFoam -postProcess -func age
此时在每个时间文件夹下增添了名为age的文件。

5.2 监测物理量
可以准备监测文件获取检测位置的age值。
如创建两个监测文件probes1及probes2,其内容分别为:
// probes1
#includeEtc "caseDicts/postProcessing/probes/probes.cfg"
fields (age);
probeLocations
(
(1.13 1.8 0.0)
(1.13 1.8 0.1)
(1.13 1.8 0.2)
(1.13 1.8 0.3)
(1.13 1.8 0.4)
(1.13 1.8 0.5)
(1.13 1.8 0.6)
(1.13 1.8 0.7)
(1.13 1.8 0.8)
(1.13 1.8 0.9)
(1.13 1.8 1.0)
(1.13 1.8 1.1)
(1.13 1.8 1.2)
(1.13 1.8 1.3)
(1.13 1.8 1.4)
(1.13 1.8 1.5)
(1.13 1.8 1.6)
(1.13 1.8 1.7)
(1.13 1.8 1.8)
(1.13 1.8 1.9)
(1.13 1.8 2.1)
(1.13 1.8 2.2)
(1.13 1.8 2.3)
(1.13 1.8 2.4)
(1.13 1.8 2.5)
(1.13 1.8 2.6)
(1.13 1.8 2.7)
(1.13 1.8 2.8)
(1.13 1.8 2.9)
(1.13 1.8 3.0)
);
probes2文件如下所示。
#includeEtc "caseDicts/postProcessing/probes/probes.cfg"
fields (age);
probeLocations
(
(3.2 1.8 0.0)
(3.2 1.8 0.1)
(3.2 1.8 0.2)
(3.2 1.8 0.3)
(3.2 1.8 0.4)
(3.2 1.8 0.5)
(3.2 1.8 0.6)
(3.2 1.8 0.7)
(3.2 1.8 0.8)
(3.2 1.8 0.9)
(3.2 1.8 1.0)
(3.2 1.8 1.1)
(3.2 1.8 1.2)
(3.2 1.8 1.3)
(3.2 1.8 1.4)
(3.2 1.8 1.5)
(3.2 1.8 1.6)
(3.2 1.8 1.7)
(3.2 1.8 1.8)
(3.2 1.8 1.9)
(3.2 1.8 2.1)
(3.2 1.8 2.2)
(3.2 1.8 2.3)
(3.2 1.8 2.4)
(3.2 1.8 2.5)
(3.2 1.8 2.6)
(3.2 1.8 2.7)
(3.2 1.8 2.8)
(3.2 1.8 2.9)
(3.2 1.8 3.0)
);
执行命令:
postProcess -func probes1 -latestTime
postProcess -func probes2 -latestTime
此时在文件夹postProcessing中新增两个文件名分别为probes1、probes2的文件夹,其中放置了获取的age数据。如下图所示。

该文件可以通过文本编辑器打开,里面列出了监测的各位置点的age值。

6 后处理
可以使用下面的命令查看计算残差:
foamMonitor -l postProcessing/residuals/0/residuals.dat
计算残差如下图所示。

y=0面上age分布

y=0面上速度分布

---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
版权声明:
原创文章,来源CFD之道,本文已经授权,欢迎分享,如需转载请联系作者。